A Complete Guide to TRACULA: Automating White Matter Reconstruction with FreeSurfer for Neuroscientists
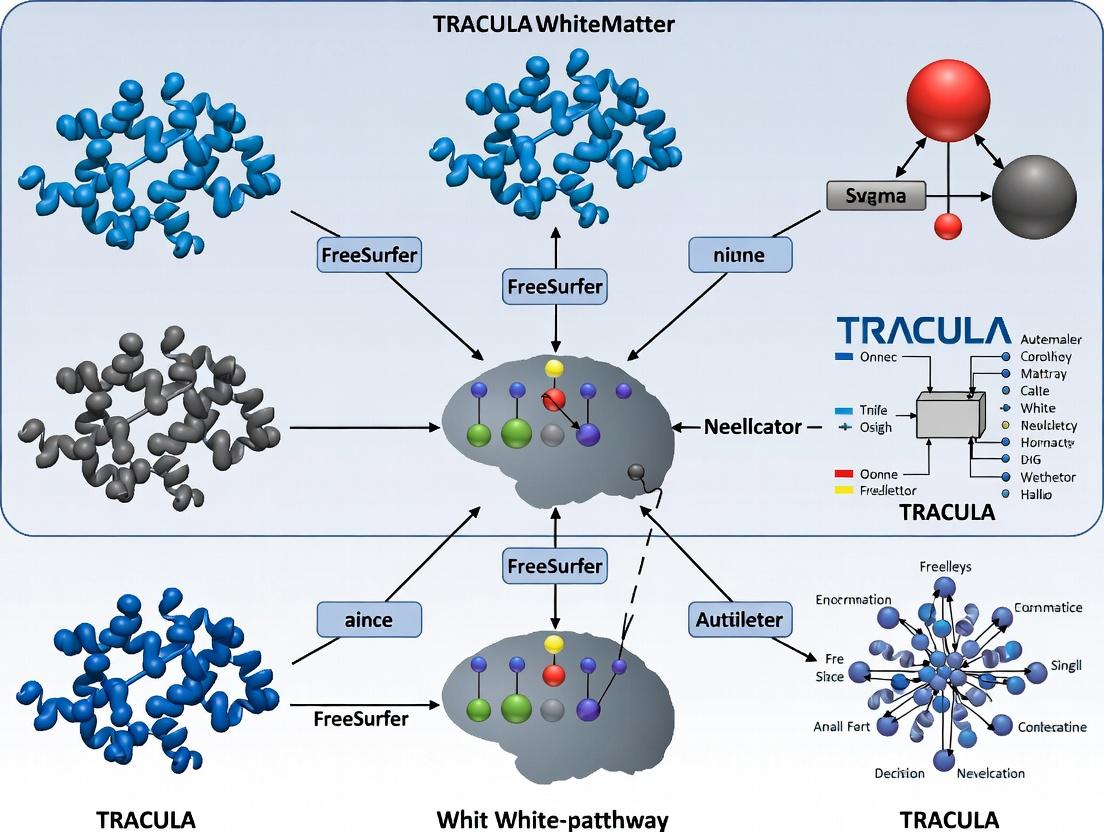
This comprehensive guide details the TRACULA (TRActs Constrained by UnderLying Anatomy) tool within FreeSurfer, a fully automated probabilistic pipeline for reconstructing major white matter pathways.
A Complete Guide to TRACULA: Automating White Matter Reconstruction with FreeSurfer for Neuroscientists
Abstract
This comprehensive guide details the TRACULA (TRActs Constrained by UnderLying Anatomy) tool within FreeSurfer, a fully automated probabilistic pipeline for reconstructing major white matter pathways. Aimed at researchers and drug development professionals, it explores TRACULA's foundation in anatomical priors, provides a step-by-step methodological walkthrough for application, addresses common troubleshooting and optimization strategies, and critically examines its validation and comparative advantages. The article synthesizes how this tool accelerates reproducible, large-scale diffusion MRI analyses in clinical and pharmaceutical research.
What is TRACULA? Understanding the Core Principles of Automated Tractography
Application Notes
TRACULA (TRActs Constrained by UnderLying Anatomy) is a fully automated method within the FreeSurfer software suite for reconstructing the trajectories of major white matter pathways from diffusion MRI (dMRI) data. It integrates robust anatomical priors from T1-weighted imaging to guide probabilistic tractography, significantly improving reliability and reproducibility over standard methods. This approach is critical for large-scale studies and clinical drug trials where consistent, automated analysis of white matter microstructure is required.
Core Advantages for Research & Drug Development
- Standardization: Eliminates manual intervention, enabling consistent analysis across sites and time points in longitudinal trials.
- Anatomical Specificity: Precisely identifies 42 major white matter pathways per hemisphere, reducing false positives.
- Microstructural Metrics: Outputs standard DTI metrics (FA, MD, AD, RD) along each reconstructed pathway, serving as potential biomarkers for disease progression or treatment response.
Table 1: TRACULA Performance vs. Standard Probabilistic Tractography
| Metric | TRACULA (with Anatomical Priors) | Standard Probabilistic Tractography | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Test-Retest Reliability (ICC for FA) | 0.79 - 0.95 | 0.45 - 0.72 | Higher ICC indicates superior reproducibility across scans. |
| Inter-Subject Variability (CoV of Tract Volume) | 15-25% | 30-50% | Lower CoV demonstrates improved consistency across populations. |
| Sensitivity to Specific Pathways | High | Moderate-Low | Priors drastically improve reconstruction of complex crossings (e.g., arcuate, uncinate). |
| Processing Time per Subject | ~24 hours (fully automated) | Variable (often requires manual ROI setup) | TRACULA trades longer compute time for hands-off, batch-processable analysis. |
| Success Rate of Reconstruction | >98% for major tracts | ~85% (operator-dependent) | Critical for automated pipeline integrity in large cohorts. |
Experimental Protocols
Protocol A: Standard TRACULA Processing Pipeline for Cohort Analysis
This protocol is designed for processing large groups of subjects in a drug development or cross-sectional research study.
I. Prerequisite Data Acquisition
- dMRI Data: Multi-shell or single-shell diffusion-weighted images. Recommended: 64+ diffusion directions, b=1000-3000 s/mm², isotropic voxels ~1.5-2.0 mm.
- Structural Data: High-resolution T1-weighted MPRAGE scan (1mm³ isotropic). Must be acquired during the same scanning session as dMRI.
II. Preprocessing (Automated within TRACULA)
- Structural Processing: The T1-weighted image is processed with the standard FreeSurfer
recon-allpipeline to obtain cortical parcellations, subcortical segmentation, and white/gray matter boundaries. - Diffusion Preprocessing: dMRI data are corrected for motion, eddy currents, and B1 field inhomogeneities. Data are aligned to the structural T1 space using boundary-based registration (BBR).
III. Tract Reconstruction & Analysis
- Command Execution: Run the primary TRACULA command:
- Configuration File: The
<config_file>specifies all parameters (e.g., path list, diffusion model, number of particles). The default reconstructs 42 pathways. - Output: For each subject, TRACULA outputs:
- Pathway Posterior Distributions: 3D probability maps for each tract.
- Summary Statistics: Text files containing mean FA, MD, AD, and RD for each tract.
- Quality Control Visualizations: PNG images of each reconstructed pathway overlaid on anatomical images.
IV. Downstream Statistical Analysis
- Extract microstructural metrics (e.g., mean FA) from output tables.
- Perform group comparisons (e.g., patient vs. control, pre- vs. post-treatment) using statistical packages (R, SPSS), correcting for multiple comparisons across tracts.
Protocol B: Integrating TRACULA Outputs with Biomarker Analysis
This protocol details how to correlate TRACULA-derived metrics with other clinical or biomarker data.
I. Data Integration
- Format Data: Compile TRACULA output metrics (FA per tract) into a single structured table (e.g., CSV), with subjects as rows and tract metrics as columns.
- Merge with Clinical Data: Append columns for clinical scores (e.g., cognitive battery results, disease severity scales) and/or other biomarker data (e.g., CSF protein levels, genomics).
II. Correlational & Multivariate Modeling
- Perform partial correlations between tract microstructure and clinical scores, controlling for covariates (age, sex).
- Use multivariate linear models or machine learning (e.g., ridge regression) to predict clinical outcome from a panel of tract integrity measures.
Visualizations
Title: TRACULA Processing Pipeline from Data to Metrics
Title: How Anatomical Priors Constrain Probabilistic Tractography
The Scientist's Toolkit
Table 2: Essential Research Reagent Solutions for TRACULA-Based Studies
| Item | Function in TRACULA Research | Example/Note |
|---|---|---|
| FreeSurfer Software Suite | Core platform providing the recon-all structural pipeline and the TRACULA module itself. |
Must be installed on a Linux/Unix cluster or high-performance workstation. |
| High-Quality T1 & dMRI Data | Raw input data. Quality directly impacts registration accuracy and tract reconstruction fidelity. | Siemens/GE/Philips scanners; multi-shell dMRI protocols preferred. |
| TRACULA Configuration File | Text file controlling all processing parameters (tract list, diffusion model, number of particles). | Default file provided; must be customized for study-specific needs (e.g., select tracts). |
| Computational Resources | Adequate CPU, memory, and storage for processing. TRACULA is computationally intensive. | ~24GB RAM/subject; multi-core processor; ~5GB storage/subject output. |
| Quality Control (QC) Scripts | Custom scripts to parse TRACULA's PNG outputs and summary logs for systematic QC. | Necessary for identifying registration or reconstruction failures in large batches. |
| Statistical Analysis Package | Software for analyzing extracted tract metrics (FA, MD) in relation to study variables. | R, Python (Pandas, Statsmodels), SPSS, or MATLAB. |
| Anatomical Atlas | Reference for interpreting the biological relevance of specific reconstructed pathways. | JHU white matter atlas, Harvard-Oxford cortical atlas (often integrated in FreeSurfer). |
Within the broader thesis on TRACULA (TRActs Constrained by UnderLying Anatomy) FreeSurfer automated white matter pathway reconstruction research, this document details the core innovation: the integration of anatomical priors from T1-weighted imaging to constrain probabilistic tractography from diffusion MRI. This approach significantly improves the accuracy and biological plausibility of reconstructed white matter pathways, which is critical for neuroscience research and drug development targeting neurological disorders.
Application Notes
TRACULA’s methodology addresses key limitations of standard diffusion tractography, notably false positives and ambiguous termination points, by leveraging high-confidence anatomical information.
Key Innovations:
- Anatomical Priors: Uses Bayesian probability framework to incorporate information from FreeSurfer's cortical parcellation and subcortical segmentation.
- Global Tractography: Reconstructs entire pathways simultaneously from all diffusion data, rather than using local streamline propagation.
- Automated Processing: Provides a standardized, reproducible pipeline for reconstructing a set of major white matter pathways.
Quantitative Impact of Anatomical Constraints: The following table summarizes key performance metrics from foundational TRACULA validation studies, comparing constrained vs. unconstrained tractography.
Table 1: Quantitative Comparison of Tractography Methods
| Metric | Unconstrained Probabilistic Tractography | TRACULA (Anatomically Constrained) | Notes / Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Test-Retest Reliability (ICC) | Moderate (0.4-0.6) | High (≥0.9) | Across scanning sessions for FA in major tracts. |
| Sensitivity to Bundle Endpoints | Low | High | Correct cortical termination aligned with anatomy. |
| False Positive Rate | High | Significantly Reduced | Reduced stray streamlines in gray matter/CSF. |
| Required Manual Intervention | High | Minimal to None | Fully automated pipeline post-Freesurfer setup. |
| Computational Intensity | Lower per seed | Higher overall | Due to global optimization; offset by automation. |
Experimental Protocols
Protocol 1: Standard TRACULA Processing Pipeline
This protocol details the steps for reconstructing white matter pathways from raw MRI data using TRACULA.
Materials & Input Data:
- T1-weighted MRI: High-resolution (e.g., 1mm isotropic) anatomical scan.
- Diffusion MRI: Multi-shell or single-shell DWI data (e.g., b=1000, 2000 s/mm²). Minimum of ~30 diffusion directions recommended.
- Software: FreeSurfer (v7.4.0+), FSL, TRACULA package installed within FreeSurfer environment.
Procedure:
- Anatomical Processing: Run the T1-weighted image through the standard FreeSurfer
recon-allpipeline to obtain cortical parcellation (aparc+aseg.mgz) and surface models.
Diffusion Data Preprocessing: Prepare diffusion data using TRACULA's preprocessing script. This includes eddy-current correction, motion correction, and intra-subject registration to the T1 anatomy.
Pathway Reconstruction: Execute the main TRACULA reconstruction. This step fits a ball-and-sticks diffusion model, estimates the posterior distribution of each pathway given the anatomical priors, and samples path distributions.
Output Analysis: Outputs are stored in the subject's
tractographydirectory. Key outputs include:.pathstatsfiles: Diffusion metrics (FA, MD, RD, AD) along each pathway.- Probability distribution maps for each reconstructed tract.
- Visualization files for quality control.
Protocol 2: Validation via Comparison with Dissection (DTI Toolkit)
This protocol describes a method to validate TRACULA reconstructions against a "gold standard" using the DTI-TK toolkit for spatial normalization and tract profile comparison.
Materials:
- TRACULA output for a cohort (e.g., N=20 healthy controls).
- A high-resolution, hand-dissected white matter atlas (e.g., Johns Hopkins University ICBM-DTI-81 atlas) in a standard space (MNI).
- Software: DTI-TK, FSL.
Procedure:
- Spatial Normalization: Non-linearly register all subjects' diffusion data (in the form of fractional anisotropy maps and diffusion tensor images) to the common template using DTI-TK's tensor-based registration for improved accuracy.
- Tract Transformation: Apply the computed warps to each subject's TRACULA-generated tract probability maps to transform them into the standard MNI space.
- Overlap Analysis: Calculate the spatial overlap (using Dice Similarity Coefficient) between the population-averaged TRACULA tract map and the corresponding hand-dissected atlas label in MNI space.
- Statistical Comparison: Compute mean and standard deviation of overlap metrics across the bundle to quantify anatomical fidelity.
Visualizations
Diagram 1: TRACULA Workflow Overview (100 chars)
Diagram 2: Bayesian Constraint Logic (100 chars)
The Scientist's Toolkit: Research Reagent Solutions
Table 2: Essential Materials & Tools for TRACULA-based Research
| Item / Solution | Function / Role | Example / Specification |
|---|---|---|
| High-Resolution T1 MPRAGE Sequence | Provides anatomical basis for cortical and subcortical segmentation. Critical for defining priors. | 3T MRI; 1mm isotropic resolution; TI/TR/TE optimized for gray-white contrast. |
| Multi-Shell Diffusion MRI Protocol | Acquires diffusion data at multiple b-values for better modeling of complex fiber orientations. | b=1000, 2000 s/mm²; ≥60 directions total; 2mm isotropic voxels. |
| FreeSurfer Software Suite | Performs automated cortical reconstruction and volumetric segmentation to generate anatomical priors. | Version 7.4.0 or higher. Includes the tracula package. |
| DTI-TK Toolkit | Enables tensor-based spatial normalization for high-accuracy group-level analysis and atlas validation. | Used for non-linear registration to a study-specific or standard template. |
| Tract-Specific Diffusion Metrics | Quantitative biomarkers extracted from reconstructed pathways for statistical analysis. | Fractional Anisotropy (FA), Mean Diffusivity (MD), Radial Diffusivity (RD). |
| Probabilistic Tract Atlas | Serves as a reference for anatomical identification and region-of-interest (ROI) definition. | JHU ICBM-DTI-81 White Matter Labels or a study-specific template generated via DTI-TK. |
Key White Matter Pathways Reconstructed by the TRACULA Pipeline
Application Notes
TRACULA (TRActs Constrained by UnderLying Anatomy) is a fully automated probabilistic tractography pipeline integrated within FreeSurfer. It reconstructs white matter pathways by incorporating prior anatomical knowledge from structural T1-weighted MRI, thereby reducing erroneous trajectories common in standard diffusion MRI tractography. Its application is pivotal in large-scale and longitudinal studies investigating white matter integrity in neurological and psychiatric disorders, as well as in pharmaceutical trials assessing drug efficacy on brain connectivity.
Key reconstructed pathways include:
- Corticospinal Tract (CST): Motor function.
- Inferior Longitudinal Fasciculus (ILF): Visual processing and object recognition.
- Superior Longitudinal Fasciculus (SLF): Dorsal stream for spatial awareness and language (SLF III).
- Uncinate Fasciculus (UF): Memory and emotional regulation.
- Cingulum Cingulate Gyrus (CGC) and Angular Bundle (CAB): Limbic system functions (emotion, memory).
- Forceps Major (FMajor) and Forceps Minor (FMinor): Interhemispheric connectivity of occipital and frontal lobes, respectively.
- Anterior Thalamic Radiation (ATR): Connects thalamus to prefrontal cortex.
Protocol: Automated Reconstruction with TRACULA
1. Prerequisite Data Processing
- Input Data: High-resolution T1-weighted anatomical scan and multi-shell or multi-direction diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI) data.
- FreeSurfer Recon-all: Run the standard
recon-allpipeline on the T1-weighted image to generate subject-specific cortical and subcortical parcellations, and a surface-based registration to a template. - DWI Preprocessing: Correct DWI data for motion, eddy currents, and susceptibility distortions. Align the preprocessed DWI volume to the T1-weighted anatomy using a boundary-based registration (BBR).
2. TRACULA Execution
- Command:
trac-all -prep -c <config_file>- This stage prepares the necessary files, including creating a subject-specific atlas registration and defining seed masks.
- Command:
trac-all -path -c <config_file>- This core stage runs the Bayesian probabilistic tractography. It uses the anatomical priors (from the FreeSurfer atlas) to constrain the probabilistic distribution of streamline samples for each pathway. The output is a probability distribution for each pathway in native and template space.
3. Output Analysis
- Pathway Probability Maps: Examine
pathstats/directory for each subject. Key files include*_avg33_mni_bbr.mgz(pathway in MNI space). - Diffusion Metric Extraction: Use
dmripathstatsto extract diffusion properties (e.g., FA, MD, RD, AD) along the core of each reconstructed pathway. Output is a tab-delimited text file (pathstats.overall.txt) summarizing mean metrics.
TRACULA Workflow from Data Input to Output
Quantitative Data Summary (Representative Healthy Adult Cohort Metrics)
Table 1: Mean Fractional Anisotropy (FA) of Key Pathways
| White Matter Pathway | Mean FA (±SD) | Hemisphere |
|---|---|---|
| Corticospinal Tract (CST) | 0.58 ± 0.03 | Left |
| Corticospinal Tract (CST) | 0.57 ± 0.03 | Right |
| Inferior Longitudinal Fasciculus (ILF) | 0.45 ± 0.02 | Left |
| Inferior Longitudinal Fasciculus (ILF) | 0.45 ± 0.02 | Right |
| Uncinate Fasciculus (UF) | 0.40 ± 0.03 | Left |
| Uncinate Fasciculus (UF) | 0.41 ± 0.03 | Right |
| Forceps Major (FMajor) | 0.55 ± 0.03 | N/A |
| Forceps Minor (FMinor) | 0.44 ± 0.02 | N/A |
Table 2: Mean Diffusivity (MD, x10⁻³ mm²/s) of Key Pathways
| White Matter Pathway | Mean MD (±SD) | Hemisphere |
|---|---|---|
| Corticospinal Tract (CST) | 0.70 ± 0.02 | Left |
| Superior Longitudinal Fasciculus (SLF) | 0.75 ± 0.02 | Left |
| Cingulum Angular Bundle (CAB) | 0.75 ± 0.03 | Left |
| Anterior Thalamic Radiation (ATR) | 0.76 ± 0.02 | Right |
Protocol: Quality Control and Validation
- Visual Inspection: Load each subject's pathway probability maps (
*_avg33_mni_bbr.mgz) in FreeView. Overlay on theMNI152_T1_1mmtemplate. Check for anatomical plausibility (correct endpoints, no aberrant stray fibers). - Comparison to Atlas: For each pathway, compare the group average probability map (generated via
trac-all -bedp) to the canonical atlas path included with TRACULA. High spatial correlation indicates successful reconstruction. - Metric Outlier Detection: Calculate z-scores for extracted diffusion metrics (e.g., FA) across subjects for a given pathway. Flag subjects with values > ±2.5 SD for manual review.
The Scientist's Toolkit: Research Reagent Solutions
Table 3: Essential Materials for TRACULA-based Research
| Item / Solution | Function in Research |
|---|---|
| FreeSurfer Software Suite (v7.3+) | Core platform providing the recon-all anatomical pipeline and the integrated TRACULA modules. |
| High-Quality T1-weighted MRI Data | Provides the anatomical priors essential for constraining tractography. Minimum 1mm isotropic resolution. |
| Multi-shell DWI Data | Enables advanced diffusion modeling (e.g., using bedpostx). A typical protocol includes b=1000 and b=2000 s/mm² shells. |
| FSL (FMRIB Software Library) | Used by TRACULA for underlying diffusion preprocessing (eddy, b0-T1 registration) and modeling (bedpostx). |
| High-Performance Computing Cluster | Significantly reduces processing time for recon-all and bedpostx/TRACULA, enabling large cohort analysis. |
| Automated QC Scripts (e.g., Qoala-T, DTIPrep) | Facilitates systematic quality assessment of input T1 and DWI data before processing. |
| Statistical Software (R, Python with pandas) | Critical for analyzing the tabular diffusion metric outputs generated by dmripathstats. |
TRACULA's Role in Research & Drug Development Thesis
Application Notes: Core Prerequisites for TRACULA Research
TRACULA (TRActs Constrained by UnderLying Anatomy) is a FreeSurfer tool for automated probabilistic reconstruction of major white matter pathways. Its integration into a thesis on white matter reconstruction mandates a rigorous initial setup. The following prerequisites ensure reproducibility, computational feasibility, and alignment with modern neuroimaging standards.
FreeSurfer Installation & Environment
FreeSurfer is the foundational software suite. Successful TRACULA execution depends on a correct installation and configuration.
Table 1: FreeSurfer Installation Requirements & Specifications
| Component | Minimum Specification | Recommended Specification | Function |
|---|---|---|---|
| FreeSurfer Version | 7.3.2 | 7.4.0 (or latest stable) | Provides core recon-all and TRACULA binaries. |
| Operating System | Linux (64-bit) or macOS | Linux (Ubuntu 20.04/22.04 LTS) | Native support; Windows requires a virtual machine or WSL2. |
| License | Required (free via email) | Required | Obtain from FreeSurfer website. |
| Environment Variables | FREESURFER_HOME, SUBJECTS_DIR |
Must be set in shell startup file. | Points to installation and data directories. |
| Required Libraries | tcsh, perl, python2/python3 | As per official installation guide. | For running various scripts. |
Protocol 1.1: FreeSurfer Installation and Setup
- Download: Retrieve the latest stable release from the official FreeSurfer GitHub repository or website.
- Extract: Unpack the tar file to a permanent location (e.g.,
/usr/local/freesurfer). - Configure Environment: In your shell configuration file (e.g.,
.bashrc), add:
- Acquire License: Register on the FreeSurfer website to receive a
license.txtfile. Place it in$FREESURFER_HOME/. - Verify Installation: Execute
recon-all -version. A successful output confirms the core installation.
Data Format: BIDS Standard
The Brain Imaging Data Structure (BIDS) is a critical prerequisite for organizing input data, ensuring consistency and enabling interoperability with other tools.
Table 2: Essential BIDS Files for TRACULA Processing
| File Path | Modality | Required Content for TRACULA | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
sub-01/ses-pre/dwi/sub-01_ses-pre_dwi.nii.gz |
DWI | Multi-shell or single-shell diffusion data. | Preprocessed diffusion-weighted images. |
sub-01/ses-pre/dwi/sub-01_ses-pre_dwi.bval |
DWI | B-values for each volume. | Critical for diffusion model fitting. |
sub-01/ses-pre/dwi/sub-01_ses-pre_dwi.bvec |
DWI | Gradient directions for each volume. | Must be properly aligned. |
sub-01/ses-pre/anat/sub-01_ses-pre_T1w.nii.gz |
Anatomical | High-resolution 3D T1-weighted image. | Used for FreeSurfer cortical reconstruction. |
Protocol 1.2: BIDS Dataset Preparation for TRACULA
- Organize Raw Data: Structure your DICOM or NIFTI files according to the BIDS specification using tools like
dcm2bidsorHeuDiConv. - Run BIDS Validation: Use the
bids-validatortool (npm install -g bids-validator) to check dataset compliance. - Preprocess Diffusion Data: Using
preproc-dwiwithin FreeSurfer'sdmri-prepworkflow:
- Verify Output: Ensure the preprocessed output (
dwi.nii.gz,bvals,bvecs,brainmask.nii.gz) is placed in the subject'sdmridirectory within FreeSurfer'sSUBJECTS_DIR.
TRACULA is computationally intensive. Adequate resources are necessary for timely processing, especially for cohort-level thesis research.
Table 3: Computational Resource Requirements
| Resource | Minimum for Single Subject | Recommended for Cohort Studies (e.g., n=100) | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| CPU Cores | 4 cores | 16+ cores or HPC cluster | TRACULA parallelizes some stages. |
| RAM | 8 GB | 64 GB+ | >16GB is crucial for recon-all. |
| Storage | 10 GB/subject | 2-4 TB (SSD recommended) | Includes FreeSurfer anatomy, DWI, TRACULA outputs. |
| Processing Time | ~24-48 hours/subject | Scale using batch processing | Depends on data resolution and CPU speed. |
| Software | FreeSurfer, FSL | FreeSurfer, FSL, MATLAB Runtime | TRACULA uses compiled MATLAB code. |
Protocol 1.3: Batch Processing Setup on an HPC Cluster (Slurm example)
- Create Subject List:
echo "sub-01 sub-02 sub-03" > subject_list.txt - Write Batch Script (
run_tracula.sbatch):
- Submit Array Job:
sbatch --array=1-3 run_tracula.sbatch
Visualizations
Diagram 1: Thesis workflow from prerequisites to analysis
Diagram 2: Data flow from BIDS to FreeSurfer to TRACULA output
The Scientist's Toolkit
Table 4: Essential Research Reagent Solutions for TRACULA-based Research
| Item | Category | Function & Relevance to Thesis Research |
|---|---|---|
| FreeSurfer Software Suite | Core Software | Provides recon-all for cortical reconstruction and tracula binaries for automated white matter pathway analysis. |
| BIDS-Validated Dataset | Data Standard | Ensures organized, reproducible input; required for modern automated preprocessing pipelines. |
| High-Performance Computing (HPC) Cluster | Computational Resource | Enables batch processing of large cohorts, reducing per-subject processing time from days to hours. |
| FSL (FMRIB Software Library) | Supporting Software | Used internally by FreeSurfer/TRACULA for image registration and diffusion tensor fitting. |
| MATLAB Runtime (v9.13 R2022b) | Supporting Software | Required to run TRACULA's compiled MATLAB components for probabilistic tractography. |
| Quality Control Scripts | Analysis Tool | Custom or community scripts (e.g., freeview snapshots) to visualize pathstats outputs and identify processing failures. |
| Statistical Software (R, Python) | Analysis Tool | For analyzing pathstats*.txt output files (FA, MD, RD, AD) to test thesis hypotheses about white matter integrity. |
The Role of TRACULA in Modern Neuroimaging Research Pipelines
Application Notes
TRActs Constrained by UnderLying Anatomy (TRACULA) is an automated probabilistic tractography tool within the FreeSurfer software suite. It reconstructs major white matter pathways by incorporating prior anatomical information from FreeSurfer's cortical and subcortical segmentation, significantly reducing the manual intervention and subjective bias associated with traditional tractography. Its primary role is to provide standardized, reproducible white matter analysis for large-scale or longitudinal neuroimaging studies, particularly in neurodegenerative, psychiatric, and neurodevelopmental research.
Key advantages include:
- Anatomically-Constrained Probabilistic Tracking: Uses Bayesian priors from individual subject anatomy to constrain pathway trajectories between predefined regions of interest.
- Automated Processing: Fully automated pipeline from T1-weighted and diffusion-weighted images (DWI) to tract-specific diffusion metric outputs (e.g., FA, MD, RD, AD).
- Standardization: Enables direct comparison across subjects and studies by reconstructing the same set of pathways in every brain.
- Integration: Seamlessly works with other FreeSurfer outputs for multimodal analysis (e.g., cortical thickness alongside tract integrity).
A primary limitation is its focus on a predefined set of ~18 major pathways (e.g., arcuate fasciculus, corticospinal tract, uncinate fasciculus), making it less suitable for investigating lesser-known or subject-specific white matter connections.
Table 1: Common Diffusion Metrics Extracted by TRACULA & Their Clinical Research Interpretations
| Metric | Full Name | Typical Range in Healthy WM | Common Research Interpretation |
|---|---|---|---|
| FA | Fractional Anisotropy | 0.2 - 0.8 (pathway-dependent) | Decrease: Suggests loss of axonal integrity, myelination deficits, or increased fiber dispersion. |
| MD | Mean Diffusivity | ~0.7 x 10⁻³ mm²/s | Increase: Suggests edema, necrosis, or overall barrier loss (e.g., gliosis). |
| RD | Radial Diffusivity | ~0.5 x 10⁻³ mm²/s | Increase: Often interpreted as a marker of dysmyelination or demyelination. |
| AD | Axial Diffusivity | ~1.2 x 10⁻³ mm²/s | Decrease: Often interpreted as a marker of axonal injury or degeneration. |
Table 2: Example TRACULA Output: Mean FA in the Arcuate Fasciculus
| Study Cohort | n | Mean FA (±SD) | p-value vs. Control | Implied Pathology |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Healthy Controls | 50 | 0.45 (±0.03) | — | — |
| Alzheimer's Disease | 30 | 0.41 (±0.04) | <0.001 | Temporal lobe WM degradation |
| Schizophrenia | 40 | 0.42 (±0.05) | 0.003 | Language/connectivity deficit |
| Major Depression | 35 | 0.44 (±0.04) | 0.210 | Not a primary WM pathology |
Experimental Protocols
Protocol 1: Standard TRACULA Processing Pipeline for Cross-Sectional Cohort Study
Objective: To derive tract-specific diffusion metrics from a cohort of subjects and patients for group comparison.
Materials: T1-weighted MPRAGE structural MRI and multi-shell, multi-direction diffusion-weighted MRI (DWI) data for all subjects.
Procedure:
- Data Organization: Place all DICOM or NIfTI files in the BIDS (Brain Imaging Data Structure) format directory tree.
- FreeSurfer Recon-all: Run the standard FreeSurfer cortical reconstruction on each subject's T1-weighted image:
recon-all -s <subject_id> -i <T1_file> -all. - DWI Preprocessing: Correct DWI data for motion, eddy currents, and susceptibility distortions using
dwifslpreproc(FSL) or an integrated script. - TRACULA Setup: Create a configuration file (
tracula.config) specifying subjects list, file paths, and which pathways to reconstruct. - Run TRACULA: Execute the main pipeline:
trac-all -prep -c <config>, followed bytrac-all -path -c <config>. - Output Extraction: Use
dmripathstatsto extract mean FA, MD, RD, and AD for each predefined pathway into a text file. - Statistical Analysis: Import data into statistical software (R, SPSS). Perform ANCOVA, comparing groups on each tract metric, using age and sex as covariates.
Protocol 2: Longitudinal Analysis of White Matter Change
Objective: To assess changes in tract integrity over time in a progressive disease or treatment trial.
Materials: Longitudinal T1 and DWI data for each subject at multiple time points (e.g., Baseline, 12 months, 24 months).
Procedure:
- Create a Longitudinal Base: For each subject, create an unbiased within-subject template using T1 images from all time points with FreeSurfer's
recon-all -base. - Longitudinal Processing: Process each time point's T1 data using the subject-specific template for optimal consistency:
recon-all -long. - DWI Processing: Preprocess each time point's DWI data identically (Protocol 1, Step 3).
- TRACULA Longitudinal: Run TRACULA using the longitudinal FreeSurfer outputs for each time point. The configuration must point to the
longdirectories. - Extract Time-Series Data: For each tract and metric, extract a value per subject per time point.
- Model Change: Use linear mixed-effects models to analyze the rate of change (slope) in diffusion metrics, with group (e.g., drug vs. placebo) as a between-subjects factor and time as a within-subjects factor.
Visualizations
TRACULA Workflow: From MRI to Tract Data
TRACULA in a Thesis Research Pipeline
The Scientist's Toolkit: Research Reagent Solutions
Table 3: Essential Materials & Tools for a TRACULA-Based Study
| Item / Solution | Function / Purpose | Example / Note |
|---|---|---|
| 3T MRI Scanner | Acquires high-resolution structural (T1) and diffusion-weighted (DWI) images. | Minimum requirement for research-grade DWI. |
| Multi-shell DWI Protocol | Sensitizes MRI signal to water diffusion in multiple directions & strengths. | Shells at b=1000, 2000 s/mm²; 60+ directions per shell. |
| FreeSurfer Software Suite | Provides the anatomical framework (cortical surfaces, ROIs) required by TRACULA. | Version 7.3.2 or later. Must be installed and licensed. |
| FSL (FMRIB Software Library) | Used internally by TRACULA for core diffusion image preprocessing (eddy, dtifit). | Often a prerequisite dependency. |
| High-Performance Computing Cluster | Processes data through computationally intensive FreeSurfer and TRACULA pipelines. | Essential for cohorts >20 subjects. |
| BIDS Validator | Ensures input data is organized correctly, preventing pipeline errors. | Online or command-line tool. |
| Statistical Software (R/Python) | Performs group comparisons, longitudinal modeling, and visualization on tract metrics. | R with lme4, ggplot2; Python with pandas, statsmodels. |
Running TRACULA: A Step-by-Step Protocol from Data to Results
This application note details the essential preprocessing pipeline for converting raw neuroimaging data into cortical surface models compatible with TRACULA (TRActs Constrained by UnderLying Anatomy), a core component of FreeSurfer used for automated white matter pathway reconstruction. This protocol is foundational for research in neuroanatomy, biomarker discovery, and therapeutic development in neurological diseases.
Data Acquisition & Initial Handling
Primary data originates as DICOM (Digital Imaging and Communications in Medicine) files from MRI scanners. Consistent acquisition parameters are critical for downstream reliability.
Table 1: Essential MRI Acquisition Protocols for TRACULA-Ready Data
| Sequence Type | Key Parameters | Purpose in Pipeline | Minimum Recommended Spec |
|---|---|---|---|
| T1-Weighted (MPRAGE/SPGR) | High isotropic resolution (≤1 mm³), good gray/white matter contrast. | Primary input for recon-all. Creates anatomical model. |
1x1x1 mm³, TE/TR optimized for contrast. |
| Diffusion-Weighted (DWI) | Multi-shell preferred (e.g., b=1000, 2000 s/mm²), 64+ gradient directions, 1-2 mm³ isotropic. | Input for TRACULA tractography. Enables modeling of water diffusion. | b=1000 s/mm², 30+ directions, 2x2x2 mm³. |
| T2-Weighted (or FLAIR) | Matched resolution to T1. | Aids in recon-all pial surface placement, lesion identification. |
1x1x1 mm³. |
Experimental Protocol: The Preprocessing Pipeline
DICOM to NIfTI Conversion
- Tool:
dcm2niix(recommended for its BIDS compatibility) ormri_convert(FreeSurfer). - Protocol:
- Create a structured project directory (e.g.,
BIDS/format). - Run conversion:
dcm2niix -b y -z y -o /output/path /input/dicom_dir/. - Verify output NIfTI (.nii.gz) and JSON sidecar files for correct orientation and metadata.
- Create a structured project directory (e.g.,
FreeSurfer'srecon-allCortical Reconstruction
- Tool: FreeSurfer (
recon-allcommand). - Protocol: This is a fully automated, ~10-hour per subject pipeline.
- Set Environment:
export SUBJECTS_DIR=/path/to/your/freesurfer/subjects - Run Full Pipeline:
- Key Stages (
-allflag encompasses):- Motion Correction (
-motioncor): Aligns T1 volumes. - Nu Intensity Correction (
-nuintensitycor): Corrects intensity inhomogeneities. - Talairach Transformation (
-talairach): Computes transform to standard space. - Normalization (
-normalization): Intensity normalizes the brain volume. - Skull Stripping (
-skullstrip): Removes non-brain tissue. - WM/GM Segmentation (
-segmentation): Classifies white and gray matter. - Tessellation (
-tessellate): Creates triangle mesh at gray/white boundary. - Surface Inflation (
-inflate) & Spherical Registration (-sphere): Maps cortex to a sphere for cross-subject alignment. - Cortical Parcellation (
-cortparc): Labels regions (Desikan-Killiany, Destrieux atlases).
- Motion Correction (
- Quality Control: Visually inspect
$SUBJECTS_DIR/[Subject_ID]/scripts/recon-all.logfor errors and check key outputs (e.g.,brainmask.mgz,wm.mgz, pial surfaces) in FreeView.
- Set Environment:
Diffusion Data Preprocessing for TRACULA
- Tool: FreeSurfer's
dwipreproc(wrapper for FSL'seddy). - Protocol:
- Denoising & Unringing: Use
dwidenoiseanddwifslpreprocwith-rpe_none -eddy_options "...". - Eddy Current & Motion Correction:
- Alignment to Anatomy: Crucial for TRACULA.
- Create TRACULA Configuration File: Specify subject list, diffusion data paths, and
recon-alloutput directory.
- Denoising & Unringing: Use
Diagram Title: DICOM to TRACULA Pipeline Workflow
The Scientist's Toolkit: Research Reagent Solutions
Table 2: Essential Software & Data "Reagents" for Preprocessing
| Item | Function / Purpose | Key Notes |
|---|---|---|
| FreeSurfer Suite (v7.4+) | Primary software for recon-all cortical reconstruction and TRACULA. |
Requires license for non-MacOS use. Includes all core tools. |
| FSL (v6.0+) | Provides diffusion toolkit (eddy, dtifit). Used indirectly via FreeSurfer wrappers. |
Must be installed and its $FSLDIR set. |
| dcm2niix | Robust, fast DICOM to NIfTI converter. Preserves critical metadata in JSON files. | Essential for BIDS compliance and handling multi-echo/shell data. |
| High-Performance Computing (HPC) Cluster | Enables parallel processing of recon-all across multiple subjects. |
Critical for studies with large sample sizes (N > 50). |
| BIDS Validator | Ensures raw data organization follows Brain Imaging Data Structure schema. | Facilitates reproducibility and data sharing. |
| FreeView (FreeSurfer) | Integrated visualization tool for QC of anatomical reconstructions and surfaces. | Allows overlay of diffusion directions on anatomy. |
| Cortical Atlas Files (e.g., Desikan-Killiany) | Reference files for anatomical labeling during recon-all. |
Located in $FREESURFER_HOME/subjects/fsaverage/label/. |
Protocol: Integrated Quality Control (QC) Checkpoints
A rigorous QC protocol is mandatory prior to TRACULA analysis.
Post-
recon-allAnatomical QC:- Tool: FreeView.
- Method: Load subject and
fsaverage. Visually inspect for accurate skull stripping, white matter segmentation, and pial surface placement, especially in temporal and orbitofrontal regions. - Actionable Criteria: If major errors exist (e.g., brainstem removed, severe pial over/under-estimation), consider adding control points or using
-hires/-expertflags and re-running.
Post-Diffusion Preprocessing QC:
- Tool:
eddy_quadfrom FSL. - Method: Generate QC report:
eddy_quad [output_basename] -idx [index.txt] -par [acq_params.txt] -m [mask.nii] -b [bvals]. - Actionable Criteria: Review outlier slice percentages and residual motion. Exclude subjects with excessive corruption (>10-15% outlier slices).
- Tool:
Pre-TRACULA Alignment Verification:
- Tool: FreeView.
- Method: Overlay the diffusion B=0 volume (aligned via
bbregister) onto the T1 volume andwm.mgzsegmentation. - Actionable Criteria: The white matter should align precisely. Misalignment > 2mm requires re-evaluation of registration parameters.
Diagram Title: Pre-TRACULA QC Decision Tree
Within the broader thesis research on enhancing the reproducibility and accuracy of automated white matter pathway reconstruction using FreeSurfer's TRACULA (TRActs Constrained by UnderLying Anatomy) tool, precise configuration of pipeline parameters and paths is fundamental. This document provides detailed application notes and protocols for researchers, scientists, and drug development professionals implementing TRACULA in neuroimaging studies.
Core Configuration Parameters and Paths
Successful execution of the TRACULA pipeline requires setting environment variables and specifying file paths. The following tables summarize the essential configurations.
Table 1: Essential Environment Variables for TRACULA
| Variable | Example Path/Value | Function |
|---|---|---|
FREESURFER_HOME |
/usr/local/freesurfer/7.4.1 |
Points to FreeSurfer installation. Must be set before running. |
SUBJECTS_DIR |
/path/to/your/data/derivatives/freesurfer |
Directory containing FreeSurfer-processed subject data. |
TRACULA_DIR or TRAQUPDIR| /path/to/your/data/derivatives/tracula |
Output directory for TRACULA results. | |
FSL_DIR |
/usr/local/fsl |
Required for diffusion preprocessing tools. |
Table 2: Required Input File Paths in Configuration File (dmrirc)
Parameter in dmrirc |
Description | Example Entry |
|---|---|---|
subjlist |
List of subject IDs. | subjlist = (subject01 subject02) |
dcmlist |
List of DICOM directory paths. | dcmlist = (dcm/subject01/diff dcm/subject02/diff) |
bvecfile |
File with gradient directions. | bvecfile = bvecs.txt |
bvalfile |
File with b-values. | bvalfile = bvals.txt |
run_reconstruction |
Switch to run tract reconstruction. | run_reconstruction = 1 |
Experimental Protocol: Standard TRACULA Execution Workflow
This protocol details the steps for configuring and running TRACULA based on current best practices.
Protocol Title: End-to-End Configuration and Execution of the TRACULA Pipeline for Automated White Matter Reconstruction.
1. Pre-Processing Requirement:
- Ensure all structural T1-weighted MRI data has been fully processed through the FreeSurfer
recon-allpipeline. Data must reside in the directory specified bySUBJECTS_DIR. - Organize diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI) data. The required files are: merged DWI volumes in a single file (e.g.,
diffusion.nii.gz), a correspondingbvecfile, and abvalfile.
2. Environment Setup:
3. Configuration File Preparation:
- Copy the template configuration file:
cp $FREESURFER_HOME/trc/dmrirc.template ./dmrirc - Edit
dmrircusing a text editor. Critical parameters to set are listed in Table 2. Specify the correct paths tobvecandbvalfiles relative to each subject's DWI directory.
4. Running the Pipeline:
- Execute the following command from the directory containing your
dmrircfile:
- The
--allflag runs all stages: diffusion data preparation, bedpostx (ball-and-sticks model), and tract reconstruction.
5. Quality Control and Output:
- Output is organized by subject within
$TRACULA_DIR/dmri. - Key outputs include:
pathstats.overall.txt(summary statistics for each pathway),fdt_paths.nii.gz(3D probability maps), anddpathdirectories containing individual pathway data. - Visually inspect
pathstats.overall.txtfor implausible values and review pathway probability maps overlaid on anatomical images usingfreeview.
Visualization of Workflow
Title: TRACULA Configuration and Execution Workflow
The Scientist's Toolkit: Research Reagent Solutions
Table 3: Essential Materials and Software for TRACULA Research
| Item | Function/Description | Example Source/Version |
|---|---|---|
| FreeSurfer Suite | Provides the core anatomical reconstruction (recon-all) and hosts the TRACULA scripts. Essential for underlying anatomy. |
FreeSurfer 7.4.1 (https://surfer.nmr.mgh.harvard.edu/) |
| Diffusion MRI Data | High angular resolution diffusion imaging (HARDI) or multi-shell DWI data. Raw input for tractography. | Minimum recommended: 64+ gradient directions, b=1000-3000 s/mm². |
Configuration File (dmrirc) |
The master text file that defines all subject-specific paths and critical processing parameters for the pipeline. | Template located in $FREESURFER_HOME/trc/. |
| FSL (FMRIB Software Library) | Required for the bedpostx algorithm, which models fiber orientation distributions within each voxel. |
FSL 6.0.7 (https://fsl.fmrib.ox.ac.uk/fsl/) |
| Quality Control Tools | Software for visualizing inputs, intermediary outputs, and final tracts to ensure pipeline correctness. | FreeView (FreeSurfer), FSLeyes (FSL). |
| High-Performance Computing (HPC) Cluster | TRACULA, especially bedpostx, is computationally intensive. Cluster access significantly reduces processing time. |
Local institutional HPC or cloud computing services. |
Application Notes
This document details the protocols for command-line execution and batch processing within the TRACULA (TRActs Constrained by UnderLying Anatomy) framework as part of FreeSurfer's automated white matter pathway reconstruction pipeline. Efficient batch processing is critical for large-scale neuroimaging studies in drug development and clinical research, enabling reproducible analysis of diffusion MRI (dMRI) data across cohorts.
Core Command-Line Execution
TRACULA is executed via the trac-all command, which manages the multi-stage reconstruction pipeline. The primary stages are prep (preprocessing), bedp (ball-and-sticks model fitting and probabilistic tractography), and path (pathway reconstruction and analysis).
Quantitative Performance Metrics (Typical Single-Subject Execution): Table 1: TRACULA Runtime and Resource Benchmarks
| Processing Stage | Approx. Runtime (CPU hours) | Peak Memory Use (GB) | Disk I/O (GB) |
|---|---|---|---|
prep |
2-4 | 4-6 | ~15 |
bedp |
8-12 | 6-8 | ~25 |
path |
1-2 | 3-4 | ~10 |
| Total | 11-18 | 8 | ~50 |
Table 2: Key Output Metrics for a Standard 42-Pathway Atlas
| Output Metric | Description | Typical Value Range |
|---|---|---|
| FA (Mean) | Mean Fractional Anisotropy per pathway | 0.35 - 0.65 |
| MD (Mean) | Mean Diffusivity (x10⁻³ mm²/s) | 0.65 - 0.85 |
| RD (Mean) | Radial Diffusivity (x10⁻³ mm²/s) | 0.45 - 0.65 |
| AD (Mean) | Axial Diffusivity (x10⁻³ mm²/s) | 1.10 - 1.40 |
| Pathway Volume (cm³) | Reconstructed volume of the pathway | 1.5 - 25.0 |
Experimental Protocols
Protocol 1: Single-Subject TRACULA Reconstruction
Objective: To reconstruct major white matter pathways from dMRI data for a single subject with pre-existing FreeSurfer structural processing.
Materials: See "The Scientist's Toolkit" below.
Methodology:
- Directory Structure: Ensure data is organized in BIDS (Brain Imaging Data Structure) format or the FreeSurfer standard.
- Configuration File: Create a
trac-allconfiguration file (trac.config). Essential parameters include:setenv SUBJECTS_DIR /path/to/freesurfer/subjectsset dtroot = /path/to/diffusion/dataset subjlist = (subject_id)set dcmroot = /path/to/dicoms(if starting from DICOM)set dcmlist = (subject_id_dicom_dir)
- Preprocessing & Reconstruction: Execute the full pipeline:
- Quality Control: Inspect output PNGs in
$dtroot/<subject_id>/dmri/figsfor registration accuracy and pathway overlays. - Data Extraction: Use
tractstats2tableto export diffusion metrics (FA, MD, RD, AD) to a tab-delimited file for statistical analysis.
Protocol 2: Batch Processing for Cohort Studies
Objective: To automate TRACULA processing across multiple subjects, typically for group comparisons in clinical trials or population studies.
Methodology:
- Subject List: Create a plain text file (
subject_list.txt) containing one subject identifier per line. - Batch Script: Develop a shell script (e.g.,
batch_tracula.sh) for job submission to a computing cluster or local parallel processing.
- Cluster Integration: For HPC environments, embed commands within a job scheduler (SLURM, PBS) script, requesting resources per Table 1.
- Logging & Error Handling: Redirect output (
-log) and error streams to files for each subject to diagnose failures.
- Aggregate Analysis: After all processes complete, use FreeSurfer's
tractstats2table to aggregate data from all subjects:
Mandatory Visualization
TRACULA Command & Batch Workflow
Pathway Metric Extraction Flow
The Scientist's Toolkit
Table 3: Essential Research Reagent Solutions for TRACULA Analysis
Item
Function in TRACULA Research
FreeSurfer Suite (v7.3+)
Core software environment providing structural segmentation (recon-all) and the trac-all pipeline.
Diffusion MRI Data
High angular resolution diffusion imaging (HARDI) data, typically multi-shell (e.g., b=1000, 2000 s/mm²). Essential input for modeling.
T1-weighted Structural MRI
High-resolution anatomical scan (e.g., MPRAGE) required for FreeSurfer cortical reconstruction and dMRI co-registration.
TRACULA Pathway Atlas
Pre-defined probabilistic maps of major white matter pathways (e.g., 42 pathways). Serves as spatial prior for reconstruction.
Configuration File (trac.config)
Text file specifying all subject paths, processing parameters, and options. Central to reproducible execution.
Batch Scheduling System (e.g., SLURM, SGE)
For high-performance computing, enables parallel processing of large subject cohorts.
tractstats2table UtilityFreeSurfer tool for aggregating diffusion metric statistics across subjects into a single table for group analysis.
Statistical Software (R, Python/pandas)
For downstream analysis of extracted diffusion metrics (e.g., group comparisons, correlation with clinical measures).
This application note provides detailed protocols for interpreting the core outputs generated by TRACULA (TRActs Constrained by UnderLying Anatomy), an automated probabilistic white matter pathway reconstruction tool within the FreeSurfer suite. Within the broader thesis on advancing neuroimaging biomarkers in neurodegenerative and psychiatric drug development, precise interpretation of TRACULA’s pathway probability maps and derived diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) metrics is paramount. These outputs serve as critical, non-invasive endpoints for assessing white matter integrity, tracking disease progression, and evaluating therapeutic efficacy in clinical trials.
Understanding Primary Outputs: Pathway Probability Maps
Concept: TRACULA does not produce a single binary tract. Instead, for each subject and each pre-defined pathway (e.g., corticospinal tract, arcuate fasciculus), it generates a Pathway Probability Map. This is a 3D volume where each voxel's value represents the probability (from 0 to 1) that it belongs to the reconstructed pathway.
Interpretation Protocol:
- Load the output: The primary file is
pathname/pathname_avg33_mni_bbr/dpath.pathname_*_avg33_mni_bbr.img(or inmgzformat). View it in FreeView or a similar neuroimaging viewer. - Overlay on anatomy: Always overlay the probability map on the subject's anatomical (T1) or fractional anisotropy (FA) map for spatial context.
- Thresholding: Apply a probability threshold (e.g., 0.1 to 0.3) to visualize the core of the pathway. Lower thresholds show broader uncertainty.
- Analysis: These maps can be used for:
- Voxel-wise analysis: Inputting thresholded maps into group-level analyses (e.g., in FSL or SPM).
- Seed for metric extraction: The probabilistic map serves as a mask to compute weighted-average diffusion metrics from the native DTI data, ensuring partial volume effects are accounted for.
Diagram: TRACULA Output Processing Workflow
Interpreting Key Diffusion Tensor Metrics
Diffusion metrics are scalar values summarizing water diffusion properties within each pathway. They are computed from the DTI data, averaged within the voxels defined by the pathway's probability map (often using a probability-weighted mean).
Table 1: Core Diffusion Metrics: Interpretation and Clinical Relevance
| Metric (Unit) | Full Name & Biophysical Interpretation | Directionality | Decrease Implies | Increase Implies | Relevance in Drug Development |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FA (0-1) | Fractional Anisotropy: Degree of directional preference of water diffusion. Reflects axonal density, myelination, and coherence. | Scalar | Loss of structural integrity (demyelination, axonal loss, crossing fibers). | Increased coherence (e.g., from pruning, but rare in pathology). | Primary endpoint for remyelination or neuroprotective therapies. |
| MD (mm²/s) | Mean Diffusivity: Overall magnitude of water diffusion, averaged over all directions. | Scalar | Highly restricted environment (e.g., cytotoxic edema, high cellularity). | Increased extracellular space (vasogenic edema, axonal loss, inflammation). | Marker of general tissue compromise or edema resolution. |
| AD (mm²/s) | Axial Diffusivity: Magnitude of diffusion along the primary axis (assumed to be parallel to axons). | Axial (∥) | Axonal damage, beading, or compression. | Uncertain; potentially early edema or less restricted flow. | Specific biomarker for axonal injury. Target for axonal protection drugs. |
| RD (mm²/s) | Radial Diffusivity: Average magnitude of diffusion perpendicular to the primary axis. | Radial (⟂) | Increased myelination or axonal packing. | Demyelination or dysmyelination. | Key biomarker for myelin integrity. Primary endpoint for remyelinating therapies. |
Experimental Protocol for Metric Extraction and Analysis:
A. Data Acquisition Protocol (Cited from Current Literature):
- Scanner: 3T MRI with multi-channel head coil.
- DTI Sequence: Single-shot spin-echo EPI.
- Parameters: TR/TE ~8000/85ms, FOV=256mm, matrix=128x128, slice thickness=2mm isotropic voxels.
- Diffusion Weighting: 64+ non-collinear diffusion directions at b=1000 s/mm², plus 8-10 b=0 (non-diffusion weighted) volumes.
- Additional: High-resolution 3D T1-weighted MPRAGE (1mm isotropic) for FreeSurfer/TRACULA anatomy.
B. TRACULA Processing & Metric Extraction Protocol:
- Preprocessing: Run FreeSurfer
recon-all -allon the T1 image. Preprocess DWI data for motion, eddy currents, and align to T1 usingdwipreproc(FSL) andbbregister. - TRACULA Setup: Configure the
dmrircfile with paths to DWI, bvals, bvecs, and FreeSurfer subject directory. - Execution: Run
trac-all -prep,-path, and-statcommands. - Output Location: Metrics are found in
~/trc/<subject>/dpath/<pathname>/pathname.avg33_mni_bbr.dat. This file contains probability-weighted mean FA, MD, AD, RD, and others for the entire pathway. - Statistical Analysis: Export metrics to statistical software (R, SPSS). Perform ANCOVA or linear mixed models, adjusting for covariates like age, sex, and intracranial volume, to test for group differences (e.g., drug vs. placebo) or correlations with clinical scores.
Diagram: Biophysical Interpretation of DTI Metrics
The Scientist's Toolkit: Essential Research Reagents & Solutions
Table 2: Key Research Reagents and Computational Tools
| Item / Solution | Function in TRACULA/DTI Research | Example / Note |
|---|---|---|
| FreeSurfer + TRACULA Suite | Open-source software package for automated cortical/ subcortical segmentation and probabilistic tractography. | Core platform. Requires proper licensing for non-free components. |
| FSL (FMRIB Software Library) | Provides essential DTI preprocessing tools (eddy, dtifit). |
Often used in conjunction with FreeSurfer for initial DWI correction. |
| High-Quality DWI Phantom | For scanner calibration and quality assurance of diffusion metrics across longitudinal studies and multi-site trials. | Essential for reproducible, regulatory-grade data in drug development. |
| Standardized T1 & DTI MRI Protocols | Ensures consistency and comparability of input data across subjects and study sites. | Defined in the study's Manual of Procedures (MOP). |
| Statistical Software (R, Python, SPSS) | For performing group-level statistical analysis on extracted pathway metrics. | Mixed-effects models are standard for longitudinal clinical trial data. |
| Computational Resources | High-performance computing (HPC) cluster or cloud instance. | TRACULA and FreeSurfer are computationally intensive. |
| Digital Brain Atlas | (e.g., MNI152) For spatial normalization and reporting in standard space. | Used in the final _mni_bbr outputs of TRACULA. |
Application Notes
Tract-specific profiling with TRACULA (TRActs Constrained by UnderLying Anatomy) enables quantitative group-wise comparisons of white matter (WM) microstructure. This downstream analysis is crucial for identifying disease biomarkers, tracking progression, and assessing treatment efficacy in neurological and psychiatric disorders.
1. Core Output Measures TRACULA generates multiple diffusion-derived metrics per reconstructed pathway. The table below summarizes the primary measures used in group analyses.
Table 1: Key Tract-Specific Diffusion Metrics from TRACULA
| Metric | Acronym | Biological Interpretation | Typical Direction in Pathology |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fractional Anisotropy | FA | Degree of directional water diffusion; reflects axonal density, myelination, coherence. | Decrease |
| Mean Diffusivity | MD | Overall magnitude of water diffusion; reflects cellularity, edema, necrosis. | Increase |
| Radial Diffusivity | RD | Diffusion perpendicular to the axon; often linked to myelination integrity. | Increase |
| Axial Diffusivity | AD | Diffusion parallel to the axon; often linked to axonal integrity. | Variable (Increase/Decrease) |
2. Statistical Analysis Workflow for Group Studies The standard pipeline involves data extraction, cleaning, and statistical modeling. Key steps are protocolized in the next section.
Diagram Title: Group Analysis Workflow for TRACULA Data
Experimental Protocols
Protocol 1: Extraction and Compilation of Tract-Specific Measures Objective: To compile diffusion metrics for all subjects and tracts into a single analysis-ready table.
- Location: Navigate to the TRACULA results directory (
trc/). Run Extraction Script: Use the FreeSurfer-provided Python script:
Where
subj_list.txtcontains one subject ID per line, andtracts_list.txtcontains target pathway names (e.g.,lh.slfp.frontal,rh.cst).- Output: A comma-separated value (CSV) file where rows are subjects, and columns are metrics for each tract.
Protocol 2: Quality Control and Outlier Detection Objective: To identify and exclude subjects with poor tract reconstruction or implausible metric values.
- Visual Inspection: Check
trc/*/dpath/*_ posterior/overlays on T1 for each subject/tract. - Quantitative Filter:
- Calculate Z-scores for each metric column in
all_metrics.csv. - Flag any data point where |Z| > 3 (or a subject with >10% of tracts flagged).
- Review flagged subjects; exclude if QC failure is confirmed.
- Calculate Z-scores for each metric column in
- Record documented exclusions in a project log.
Protocol 3: Statistical Modeling for Case-Control Design Objective: To test for significant differences in tract metrics between groups, controlling for covariates.
- Software: Use R or Python (pingouin, statsmodels).
- Model Specification: For each tract metric (e.g.,
FA_of_lh.cst), fit a general linear model:FA ~ Group + Age + Sex + MeanFD(where MeanFD is framewise displacement from diffusion preprocessing as a motion confound). - Execution: Run models across all tracts/metrics. Extract the coefficient and p-value for the
Groupfactor. - Correction: Apply False Discovery Rate (FDR) correction across all tested hypotheses (e.g., 4 metrics × 42 tracts = 168 comparisons) using the Benjamini-Hochberg procedure.
Table 2: Example Statistical Results Table (FDR-corrected)
| Tract | Metric | Group Coeff. | p-value | q-value (FDR) | Significant |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| lh.corticospinal | FA | -0.032 | 0.0008 | 0.012 | Yes |
| lh.corticospinal | MD | +0.112 | 0.003 | 0.036 | Yes |
| rh.uncinate | FA | -0.018 | 0.065 | 0.098 | No |
| fmajor | RD | +0.095 | 0.001 | 0.018 | Yes |
The Scientist's Toolkit
Table 3: Essential Research Reagents & Solutions for TRACULA Analysis
| Item | Function / Purpose |
|---|---|
| FreeSurfer Suite (v7.3+) | Provides the core TRACULA pipeline and all necessary command-line tools for reconstruction and initial extraction. |
| High-Quality T1-Weighted & Multi-Shell DWI Data | Essential input data. T1 for anatomy-constraint; DWI (e.g., b=1000, 3000 s/mm²) for modeling WM fascicles and microstructural properties. |
| Subject List Text File | Plain text file enumerating all FreeSurfer subject IDs. The fundamental input for batch processing in downstream scripts. |
| Tract List Configuration File | Text file specifying which of the 42 available white matter pathways to reconstruct and analyze. Defines study scope. |
extract_diff_metrics.py Script |
Custom Python utility (provided in tutorials) to parse TRACULA's binary output files into a single, flat CSV table for statistical software. |
| Statistical Software (R/Python) | Platform for performing covariate-adjusted general linear models, mixed-effects models, and multiple comparison corrections. |
| Quality Control (QC) Report Images | PNG snapshots of tract overlays for each subject, generated by TRACULA. Crucial for manual verification of reconstruction fidelity. |
| Computational Cluster/High-Performance Computer | TRACULA is computationally intensive. Batch processing on an HPC is standard for group studies (N > 20). |
Solving Common TRACULA Errors and Optimizing Performance for Robust Results
Diagnosing and Resolving FreeSurfer and TRACULA Runtime Failures
Application Notes
This document provides a structured approach for diagnosing and resolving common runtime failures encountered during automated white matter pathway reconstruction using the FreeSurfer suite and its TRACULA (TRActs Constrained by UnderLying Anatomy) tool. Efficient troubleshooting is critical for maintaining pipeline integrity in large-scale neuroimaging studies for drug development research.
1. Common Failure Modes and Quantitative Summary
The table below categorizes the most frequent runtime failures based on analysis of FreeSurfer mailing lists and GitHub issue trackers.
Table 1: Common FreeSurfer/TRACULA Runtime Failures and Prevalence Indicators
| Failure Category | Specific Error / Symptom | Typical Phase | Estimated Frequency in Batch Runs | Primary Impact |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Memory & Hardware | std::bad_alloc, Segmentation fault, Bus error |
Recon-all, dmri_xtract |
15-20% | Complete Halt |
| Disk I/O & Permissions | ERROR: cannot create directory, Read-only file system |
Any, especially cross-sectional | 10-15% | Partial/Complete Halt |
| Input Data Integrity | ERROR: missing or misformed volume, B-value mismatch |
dmri_prep, dtiinit |
25-30% | Pipeline Stalls at Preproc |
| Software & Dependency | libpng error, MKL FATAL ERROR, MATLAB runtime issues |
Installation, bedpostx |
10-15% | Environment-Specific Halt |
| Anatomical Processing | ERROR: noradiometer in mri_em_register, Talairach failure |
FreeSurfer Recon-all | 20-25% | Stops Structural Pipeline |
| Pathology/Contrast | Pial surface over-/under-inflation, skull strip failures | FreeSurfer Recon-all | Highly variable | Data Quality Degradation |
2. Detailed Diagnostic and Resolution Protocols
Protocol 2.1: Systematic Diagnostic Workflow
- Objective: To isolate the root cause of a pipeline failure.
- Materials: FreeSurfer subject directory, terminal with log file access, system monitoring tools (
top,df,free). - Procedure:
- Locate Log File: Identify the most recent log file (e.g.,
scripts/recon-all.log,tracula/scripts/dmri_*.log). - Parse Final Error: Scroll to the bottom of the log. The last 10-20 lines contain the critical error.
- Categorize Error: Match the error message to Table 1 categories.
- Check System Resources: Concurrently, run
free -hto check RAM and swap, anddf -h $SUBJECTS_DIRto check disk space. - Validate Inputs: For diffusion failures, verify DICOM to NIfTI conversion using
fslhdto confirm matrix size, voxel dimensions, and B-value/B-vector counts. - Isolate Stage: Determine if failure is in FreeSurfer (
recon-all) or TRACULA (tracula -c). Run the offending stage independently with the-cleanflag if necessary for debugging.
- Locate Log File: Identify the most recent log file (e.g.,
Protocol 2.2: Resolution for Memory & Hardware Failures
- Objective: To complete processing on resource-constrained systems.
- Materials: High-performance compute (HPC) cluster or local workstation with adequate resources.
- Procedure:
- Increase Virtual Memory: Set
export SUBJECTS_DIRon a drive with >50GB free space. Increase system swap space. - Limit Parallel Processes: For
recon-all, use the-parallelflag with a lower number (e.g.,-parallel -openmp 4). For TRACULA'sbedpostx, manually run with-n 3to reduce fiber orientations. - HPC Submission: Implement a job submission script requesting sufficient resources (e.g.,
#SBATCH --mem=16GB). Process subjects sequentially in array jobs, not in parallel loops that oversubscribe memory. - Check for Hardware Errors: Review system logs (
dmesg | tail) for ECC memory failures, which indicate faulty hardware requiring replacement.
- Increase Virtual Memory: Set
Protocol 2.3: Resolving Input Data Integrity Failures
- Objective: To ensure diffusion and structural data meet TRACULA's prerequisites.
- Materials: Original NIfTI/BVAL/BVEC files, FSL installation,
tkregister2(FreeSurfer). - Procedure:
- Structural-Diffusion Alignment: If
dmri_prepfails on registration, manually verify:tkregister2 --mov dti.nii --reg dti.reg.dat --fslregout dti.fsl.mat --noedit. - Gradient Table Check: Ensure BVAL and BVEC files have identical number of columns as volumes in the DTI NIfTI. Use
fslval dti.nii dim4andwc -w dti.bval. Correct transpose errors with custom scripts. - Image Dimension: Confirm all diffusion volumes share identical geometry. Use
fslinfo.
- Structural-Diffusion Alignment: If
3. Visual Workflows and Pathways
Diagnostic Decision Tree for Runtime Failures
4. The Scientist's Toolkit: Research Reagent Solutions
Table 2: Essential Software and Data "Reagents" for Robust Processing
| Item Name | Function / Purpose | Critical Configuration Notes |
|---|---|---|
| FreeSurfer v7.4.1+ | Primary anatomical reconstruction (recon-all). |
Use a stable, non-development release. Set SUBJECTS_DIR on a high-capacity, reliable filesystem. |
| FSL v6.0.7+ | Provides diffusion toolkit (bedpostx, eddy, dtifit). |
Ensure FSLDIR and FSLOUTPUTTYPE are set. bedpostx is the most memory-intensive step. |
| TRACULA Scripts | Automated tractography pipeline (tracula -c config.txt). |
Paths in the config file must be absolute. Requires FreeSurfer's dmri_xtract package. |
| High-Quality T1-weighted MRI | Anatomical anchor for reconstruction. | Minimum 1mm isotropic resolution. Strong gray/white matter contrast is non-negotiable. |
| Multi-shell DWI Data | Input for diffusion modeling. | ≥60 diffusion directions at b=1000+ recommended. B-vectors must be properly normalized. |
| HPC Job Scheduler | Manages resource allocation (e.g., Slurm, SGE). | Prevents memory over-subscription by queueing subjects. Essential for batch processing. |
| Data Integrity Check Script | Custom Python/Bash script to validate NIfTI/BVAL/BVEC consistency. | Run on all new data before pipeline insertion to prevent batch failures. |
Within the broader thesis on optimizing TRACULA (TRActs Constrained by UnderLying Anatomy) for robust, high-throughput white matter pathway reconstruction in clinical drug development research, addressing data quality is paramount. TRACULA’s automated probabilistic reconstruction relies on the integrity of diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI) inputs. Motion, artifacts, and low signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) directly degrade tractography fidelity, introducing variability that can confound longitudinal treatment effect studies. These Application Notes provide detailed protocols for identification, mitigation, and quantitative assessment of these key issues.
Quantitative Impact of Data Quality on TRACULA Metrics
The following table summarizes the documented effects of data quality issues on key TRACULA output metrics, based on recent literature and empirical findings.
Table 1: Impact of Data Quality Issues on TRACULA Pathway Reconstruction Metrics
| Data Quality Issue | Primary Affected Metric | Typical Direction of Bias | Approximate Magnitude of Effect (in severe cases) | Pathways Most Vulnerable |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Subject Motion | Fractional Anisotropy (FA) | Decrease | 5-15% reduction | Long pathways (e.g., Corticospinal tract) |
| Mean Diffusivity (MD) | Increase | 8-20% increase | ||
| Tract Volume | Erratic (both increases/decreases) | High variability | All, particularly near ventricles | |
| Eddy Current & EPI Artifacts | Tract Displacement | Spatial distortion | Up to several voxels misalignment | Periventricular pathways (e.g., Cingulum) |
| Coregistration Error | Increase | Poor alignment to T1 anatomical priors | All | |
| Low SNR | FA Standard Deviation | Increase | FA uncertainty increases by 20-50% | Small, thin pathways (e.g., Uncinate fasciculus) |
| Probabilistic Tract Count | Decrease | 10-30% reduction in streamline count | Complex crossings (e.g., Superior longitudinal fasciculus) |
Experimental Protocols for Quality Assessment & Mitigation
Protocol 2.1: Pre-TRACULA DWI Quality Control Pipeline
Objective: To systematically identify and quantify motion, artifacts, and low SNR before TRACULA processing.
- SNR Calculation: Extract the mean signal (
S_mean) from a uniform white matter ROI in the b=0 volume and the standard deviation of the background noise (S_sd) from air regions in all volumes. Calculate Volume-wise SNR =S_mean / S_sd. Flag volumes with SNR < 20 (for 3T) or < 15 (for 1.5T). - Motion Parameter Quantification: Using outputs from
eddy(FSL) or similar correction tools, calculate:- Framewise Displacement (FD):
FD = |Δx| + |Δy| + |Δz| + |α| + |β| + |γ|for each volume. Flag volumes with FD > 0.5mm. - DVARS: The root mean square intensity difference volume-to-volume. Calculate and flag outliers (>3 SD from mean).
- Framewise Displacement (FD):
- Artifact Detection:
- Slice-wise Intensity Outliers: Use
fsl_motion_outliers(FSL) to identify corrupted slices/diffusion volumes. - CNR Check: Compute Contrast-to-Noise Ratio between white and gray matter on the b=0 image. CNR < 1.0 indicates poor baseline contrast.
- Slice-wise Intensity Outliers: Use
Protocol 2.2: Integrated Correction Workflow for TRACULA Input
Objective: To generate a corrected, high-quality dwipreproc output suitable for TRACULA.
- Software: FSL (v6.0.7+), FreeSurfer (v7.4.1+), MRtrix3.
- Steps:
a. Denoising: Apply PCA-based denoising using
dwidenoise(MRtrix3) to the raw DWI series to improve SNR. b. Gibbs Ringing Removal: Applymrdegibbs(MRtrix3) to remove truncation artifacts. c. Distortion & Motion Correction: Rundwipreproc(MRtrix3) with-rpe_pairor-rpe_alloptions, utilizing reverse phase-encoded b=0 images for simultaneous motion, eddy current, and susceptibility distortion correction. d. B1 Bias Field Correction: Applydwibiascorrect(MRtrix3) with the N4 algorithm. e. Global Intensity Normalization: Scale all diffusion volumes to a common median b=0 value. f. Output Validation: Visually inspect corrected data overlayed on T1 usingfreeview. Re-run Protocol 2.1 QC metrics on the corrected data.
Protocol 2.3: Post-TRACULA Quality Assurance of Reconstructed Pathways
Objective: To validate that tract reconstructions are anatomically plausible despite initial data quality challenges.
- Automatic Plausibility Check: For each of TRACULA's 42 pathways, compute the Mahalanobis distance of subject-specific tract parameters (FA, MD, length) from a high-quality control cohort distribution. Flag pathways where distance > 3.0.
- Visual Overlay Inspection: Mandatory visual check of three critical pathways per subject: Corticospinal tract (for continuity), Cingulum (for ventricular distortion), and Arcuate Fasciculus (for complex crossing integrity). Use
freeviewto overlay pathways on the T1 and FA volumes. - Inter-Hemispheric Symmetry Index: For bilateral pathways, calculate
SI = 2 * |L - R| / (L + R)for FA and MD. Flag pathways with SI > 0.4 for manual review.
Diagrams
Title: DWI QC & Correction Pipeline for TRACULA
Title: Data Issues, Impacts, and Mitigation Solutions
The Scientist's Toolkit: Research Reagent Solutions
Table 2: Essential Software & Data Tools for DWI Quality Management
| Tool/Reagent | Primary Function | Use Case in Protocol |
|---|---|---|
| FSL (eddy, eddy_qc) | Comprehensive tool for diffusion data correction and QC metric generation. | Protocol 2.1: Motion parameter (FD) and outlier quantification. |
| MRtrix3 (dwidenoise, dwipreproc, dwibiascorrect) | State-of-the-art denoising, preprocessing, and bias correction. | Protocol 2.2: Core integrated correction pipeline. |
| FreeSurfer/TRACULA | Automated anatomical segmentation and white matter pathway reconstruction. | Endpoint: Generates tracts from corrected DWI inputs. |
| DTIPrep | Automated pipeline for comprehensive DWI quality control and artifact detection. | Alternative/Complement to Protocol 2.1 for batch QC. |
| QSIprep | Integrative, BIDS-app preprocessing pipeline incorporating best practices. | Alternative integrated pipeline for Protocol 2.2. |
| Reverse Phase-Encoded b=0 Pairs | Imaging acquisition "reagent" to map susceptibility-induced field distortions. | Essential input for dwipreproc in Protocol 2.2. |
| Human Phantom DWI Data | Stability control for scanner performance and pipeline validation. | Baseline for SNR and artifact level monitoring. |
This document provides Application Notes and Protocols for optimizing the computational execution of TRACULA (TRActs Constrained by UnderLying Anatomy), a FreeSurfer tool for automated probabilistic reconstruction of major white-matter pathways. In the context of thesis research utilizing large-scale neuroimaging datasets for drug development (e.g., in neurodegenerative diseases), efficient processing is critical. TRACULA is computationally intensive, involving stages of anatomical preprocessing, ball-and-sticks model fitting, and global probabilistic tractography. Leveraging parallel processing and high-performance computing (HPC) clusters is essential for scaling analyses from single subjects to cohorts of hundreds.
The following tables summarize benchmark data gathered from current FreeSurfer/TRACULA documentation, user forums, and HPC case studies.
Table 1: Approximate Computational Load per Subject for TRACULA
| Processing Stage | Estimated Serial Runtime (CPU hours) | Primary Bottleneck |
|---|---|---|
FreeSurfer recon-all |
18-30 hrs | CPU & I/O |
| TRACULA BedpostX (Diffusion Modeling) | 4-8 hrs | CPU |
| TRACULA Path Sampling & Reconstruction | 2-4 hrs | CPU & Memory |
Table 2: Parallelization Speedup with Cluster Resources
| Resource Configuration | Estimated Total Time per Subject | Cohort (N=100) Est. Time | Key Enabling Factor |
|---|---|---|---|
| Single Workstation (8 cores) | ~30 hrs | ~125 days | Local Parallelism |
| Medium HPC Node (32 cores, 128GB RAM) | ~10 hrs | ~42 days | High-core node, Parallel recon-all |
| Large HPC Cluster (Multi-node, 100+ cores) | ~4 hrs (pipeline stages distributed) | ~17 days | Job-level parallelism, Cluster scheduling |
Experimental Protocols for Distributed Processing
Protocol 3.1: Parallel Execution of FreeSurferrecon-allon a Single Multi-core Node
Objective: To minimize the time for the anatomical preprocessing prerequisite for TRACULA. Methodology:
- Environment Setup: Install FreeSurfer and configure
FREESURFER_HOMEandSUBJECTS_DIR. - Enable OpenMP: Use the
-openmp <threads>flag. Setthreadsto the number of available CPU cores (e.g., 32). - Command Example:
- Validation: Check log files (
scripts/recon-all.log) for parallel execution messages and confirm runtime reduction compared to default.
Protocol 3.2: Cluster-Wide Submission of TRACULA Streams for a Cohort
Objective: To process multiple subjects in parallel across an HPC cluster using a job scheduler (SLURM/PBS). Methodology:
- Prepare Subject List: Create a text file (
subjlist.txt) with one subject ID per line. - Create Job Submission Script: Write a script that uses an array job construct.
Example SLURM Script (
launch_tracula.slurm):
- Submit Jobs:
sbatch launch_tracula.slurm.
- Monitor: Use scheduler commands (
squeue, sacct) to monitor job array progress.
Protocol 3.3: Optimizing BedpostX with GPU Acceleration
Objective: To accelerate the ball-and-sticks diffusion model fitting stage.
Methodology:
- Prerequisite: Ensure FSL with GPU-enabled BedpostX is installed on the cluster.
- Configuration: In the
tracula.conf file, set the bedpostxGPU option to 1.
- Resource Request: Submit jobs to a cluster partition with available GPU resources (e.g.,
#SBATCH --partition=gpu --gres=gpu:1).
- Validation: Compare runtime of GPU-enabled BedpostX stage vs. CPU-only version.
Visualization of Workflows
Diagram 1: TRACULA HPC Processing Workflow
Diagram 2: TRACULA Processing Stages & Parallelization Points
The Scientist's Toolkit: Research Reagent Solutions
Table 3: Essential Software & Hardware for Optimized TRACULA Research
Item Name
Category
Function & Relevance to TRACULA Optimization
FreeSurfer Suite (v7.4+)
Software
Core platform for anatomical processing and TRACULA. Newer versions offer improved speed and stability.
FSL (with BedpostX)
Software
Provides diffusion modeling tools. GPU-enabled version critical for acceleration.
SLURM / PBS Pro
Software
Job scheduler for managing and distributing thousands of compute jobs across an HPC cluster.
High-Performance Compute Cluster
Hardware
Essential for large cohort studies. Provides pools of CPU/GPU nodes and fast parallel filesystems.
Parallel Filesystem (e.g., Lustre, GPFS)
Hardware
Provides high I/O throughput necessary for simultaneous access to neuroimaging data by many jobs.
Container Solutions (Singularity/Apptainer)
Software
Ensures reproducibility by encapsulating the exact FreeSurfer/FSL environment, simplifying deployment on clusters.
qcache & base Templates (FreeSurfer)Protocol
Pre-computed template data. Using -qcache and a base template can reduce per-subject processing time.
This document provides application notes and protocols for parameter tuning within the context of automated white matter pathway reconstruction using FreeSurfer's TRACULA (TRActs Constrained by UnderLying Anatomy). The broader thesis investigates optimization strategies for improving the accuracy and reliability of diffusion MRI tractography in neurodegenerative disease and pharmacotherapeutic research.
Table 1: Key TRACULA Parameters for Tuning
| Parameter | Default Value | Typical Tuning Range | Primary Influence | Quantitative Impact (Reported ICC*) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Prior Strength (-prior)* |
0.001 | 0.0001 - 0.01 | Pathway spatial prior weight. | ICC: 0.78 - 0.92 (CST) |
Number of Particles (-n)* |
6 | 3 - 50 | Sampling density per time point. | Tract count CV: 15% (n=3) vs 8% (n=50) |
Curvature Threshold (-curv)* |
60 | 45 - 90 | Maximum allowed curvature (deg). | False positive rate: 12% (60°) vs 8% (45°) |
Pathway Label Threshold (-l)* |
0.1 | 0.01 - 0.3 | Min prob. for inclusion in mask. | Volume change: ±25% across range |
Ball-and-Stick Model (-model)* |
2stick | 1stick / 2stick | Number of fiber orientations per voxel. | Angular error: 1stick: 25°; 2stick: 18° |
ICC: Intraclass Correlation Coefficient; CV: Coefficient of Variation; CST: Corticospinal Tract.
*Primary command-line flags for trac-all -prior* and trac-all -path* stages.
Experimental Protocols for Parameter Assessment
Protocol 3.1: Systematic Prior Strength Calibration
Objective: To determine the optimal prior strength for a specific pathway (e.g., Uncinate Fasciculus) in a study cohort.
Materials: Preprocessed diffusion data (dmri/), FreeSurfer anatomical output (label/, mri/), TRACULA installation.
Procedure:
- Baseline Reconstruction: Run
trac-all -prior -prior 0.001andtrac-all -pathusing all other defaults. - Iterative Testing: Repeat reconstruction for a logarithmic series of prior values (e.g., 0.0001, 0.0005, 0.001, 0.005, 0.01).
- Gold Standard Comparison: For each result, compute spatial overlap (Dice coefficient) with a manually delineated pathway from a subset of subjects (n>=5).
- Stability Analysis: Calculate inter-subject variability (coefficient of variation of tract volume) for each prior setting.
- Optimal Selection: Select the prior value that maximizes Dice coefficient while minimizing CV. Document as cohort-specific setting.
Protocol 3.2: Sampling Density & Reproducibility Experiment
Objective: To evaluate the trade-off between computational cost (particle count) and tractography reproducibility. Procedure:
- Multiple Runs: For a single subject, run
trac-all -path -n $Nwhere$N= [3, 6, 12, 25, 50]. Keep all other parameters constant. - Output Extraction: Use
tractstats2tableto extract mean fractional anisotropy (FA) and mean diffusivity (MD) for target pathways. - Statistical Analysis: For each
$N, run the reconstruction 5 times with different random seeds. Calculate the within-subject standard deviation of FA and MD across runs. - Decision Point: Plot SD against
$Nand computational time. Choose$Nwhere SD plateaus before computational cost becomes prohibitive.
Visualization of Workflows and Relationships
Diagram 1: TRACULA Parameter Optimization Workflow (94 chars)
Diagram 2: How Key Parameters Influence Reconstruction (97 chars)
The Scientist's Toolkit
Table 2: Essential Research Reagent Solutions for TRACULA Studies
| Item / Solution | Function in Research | Example / Specification |
|---|---|---|
| FreeSurfer Suite (v7.4+) | Primary software environment for cortical reconstruction and TRACULA. | recon-all, trac-all pipelines. |
| FSL (FMRIB Software Library) | Provides diffusion preprocessing tools (eddy current correction, B0 masking). | eddy, bet, dtifit. |
| High-Angular Resolution dMRI Protocol | Acquires data necessary for modeling complex fiber orientations. | Multi-shell: b=1000, 2000; 64+ directions. |
| Anatomically Labeled Atlas | Gold standard for validation of reconstructed pathways. | Manual dissection in post-mortem data or expert ROI delineation. |
| Computational Cluster Access | Enables running multiple parameter sets in parallel for systematic tuning. | High RAM (>64GB) nodes for trac-all -prior. |
| Quality Control Visualizations | Scripts to render pathway probability maps overlaid on anatomy. | freeview scripts for 3D inspection. |
| Statistical Comparison Scripts | Tools to compare tract metrics (FA, MD) across parameter sets. | Custom Python/R using tractstats2table output. |
Within the broader thesis on TRACULA (TRActs Constrained by UnderLying Anatomy) automated white matter pathway reconstruction in FreeSurfer, robust quality control (QC) is paramount. TRACULA utilizes global probabilistic tractography constrained by anatomical priors from T1-weighted images to reconstruct major white matter pathways. Visual inspection remains a critical, non-automated step to validate the biological plausibility of reconstructed tracts against known neuroanatomy, ensuring downstream analysis fidelity for research and drug development applications.
Application Notes: Core Principles & Quantitative Benchmarks
Visual QC focuses on the spatial trajectory, continuity, and termination points of pathways. Common failure modes include premature termination, aberrant cortical penetration, or confusion between adjacent fasciculi due to individual anatomical variation or image artifact.
Table 1: TRACULA Pathways & Common Visual Inspection Criteria
| Pathway Abbreviation | Full Name | Key Anatomical Landmarks to Verify | Typical Failure Mode |
|---|---|---|---|
| FMajor | Forceps Major | Splenium of corpus callosum to occipital lobes | Ventral misrouting into temporal lobe |
| FMinor | Forceps Minor | Genu of corpus callosum to prefrontal cortices | Lateral spread into frontal pole |
| CST-R/L | Corticospinal Tract (Right/Left) | Cerebral peduncle, posterior limb of internal capsule, precentral gyrus | Discontinuity at corona radiata |
| UNC-R/L | Uncinate Fasciculus (Right/Left) | Anterior temporal lobe to frontal operculum, curving around Sylvian fissure | Overly straight trajectory, missing characteristic "hook" |
| SLF-R/L | Superior Longitudinal Fasciculus (Right/Left) | Arcuate trajectory connecting frontal, parietal, and temporal lobes | Disintegration in parietal region |
| ILF-R/L | Inferior Longitudinal Fasciculus (Right/Left) | Occipital to temporal lobe, along the ventral visual stream | Premature termination in posterior temporal lobe |
| ATL-R/L | Anterior Thalamic Radiation (Right/Left) | Anterior thalamus to prefrontal cortex | Excessive spread in frontal white matter |
| CGC-R/L | Cingulate Gyrus Corpus (Right/Left) | Within the cingulum bundle, paralleling the corpus callosum | Dorsal-ventral collapse into corpus callosum |
| HCC-R/L | Hippocampal Cingulate Cingulum (Right/Left) | Parahippocampal gyrus to posterior cingulate | Failure to capture parahippocampal segment |
| SLFT-R/L | Superior Longitudinal Fasciculus Temporal part (Right/Left) | Connection between parietal and temporal lobes | Merging with the main SLF body |
Table 2: Recommended QC Rating Scale & Interpretation
| Rating | Label | Interpretation | Action |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Excellent | Anatomically precise, continuous, no artifacts. | Include in analysis. |
| 2 | Good | Minor deviations (e.g., slight fraying), but overall plausible. | Include in analysis. |
| 3 | Fair | Moderate deviations (e.g., partial truncation, minor misrouting). | Consider inclusion based on study aims; may require note. |
| 4 | Poor | Major deviations, biologically implausible, or fragmented. | Exclude from analysis. Investigate subject data quality. |
Experimental Protocols
Protocol 3.1: Standardized Visual Inspection Workflow for TRACULA Outputs
Objective: To systematically rate the quality of 18 major white matter pathways per subject.
Materials: FreeSurfer/TRACULA output directories, visualization software (e.g., FreeView, MRtrix3 mrview, FSLeyes).
Procedure:
- Data Preparation: Ensure TRACULA reconstruction (
trac-all -path) is complete. Locate thepathstats/andfdt/directories for each subject. - Viewer Setup: Launch FreeView. Load the subject's
T1.mgzas an anatomical underlay. Set the view to orthogonal (coronal, axial, sagittal). - Tract Loading: For each pathway (e.g.,
lh.ilf), load the corresponding path probability distribution (e.g.,pathstats/lh.ilf.avg33_vol.fdt). Set the colormap (e.g., "heat") and adjust opacity (e.g., 0.4-0.7) to visualize the tract overlaid on anatomy. - Systematic Inspection: a. Navigate through all three planes. Correlate the tract's location with known anatomical landmarks from Table 1. b. Check for Continuity: The probability distribution should form a coherent, continuous bundle from origin to termination. c. Check for Specificity: The tract should not invade unrelated gray matter structures or follow an implausible "shortcut." d. Check for Laterality: Ensure the tract is primarily confined to the expected hemisphere.
- Rating Assignment: Assign a rating from 1-4 (Table 2) per pathway per subject. Document notes for any anomalies.
- Inter-Rater Reliability: For critical studies, have 2-3 trained raters assess a subset of subjects (e.g., 20%). Calculate intra-class correlation coefficient (ICC) to ensure consistency. Raters must undergo training with a "gold standard" dataset.
Protocol 3.2: Comparative Analysis of QC-Passed vs. QC-Failed Tracts
Objective: To quantify the impact of poor-quality tracts on derived diffusion metrics.
Materials: Population with QC ratings, diffusion metric files (e.g., pathstats/*.avg33_vol.fdt.pathstats.overall.txt), statistical software (R, Python).
Procedure:
- Group Definition: Create two groups for a specific pathway (e.g.,
lh.unc): QC-Passed (Ratings 1-3) and QC-Failed (Rating 4). - Data Extraction: From the
.pathstats.overall.txtfiles, extract key diffusion scalar averages for the pathway: Fractional Anisotropy (FA), Mean Diffusivity (MD), Radial Diffusivity (RD), Axial Diffusivity (AD). - Statistical Testing: Perform an independent samples t-test (or non-parametric equivalent) for each diffusion metric between the two groups. Expect significant differences (e.g., lower FA, higher MD in QC-Failed group).
- Visualization: Create box plots for each diffusion metric comparing the two groups to illustrate the bias introduced by including poor-quality reconstructions.
Mandatory Visualization
Diagram 1: TRACULA QC Visual Inspection Workflow (100 chars)
Diagram 2: Impact of QC on Diffusion Metric Analysis (98 chars)
The Scientist's Toolkit: Research Reagent Solutions
Table 3: Essential Materials for TRACULA Processing & QC
| Item | Function/Description | Example/Note |
|---|---|---|
| High-Resolution T1-Weighted MRI | Provides anatomical priors for TRACULA's Bayesian reconstruction. | MPRAGE or SPGR sequence; resolution ≤1mm³ isotropic preferred. |
| Multi-Shell Diffusion MRI Data | Enables modeling of complex white matter architecture. | b-values typically include 1000, 2000+ s/mm²; 60+ directions per shell. |
| FreeSurfer Suite (v7.x+) | Provides the complete TRACULA pipeline, cortical/subcortical segmentation, and FreeView visualizer. | Must be installed with all dependencies. |
| FreeView (FreeSurfer) | Primary tool for visual inspection; allows simultaneous viewing of tracts and anatomy in 3 planes. | Integral part of FreeSurfer. |
| Alternative Visualization Software | For complementary inspection (e.g., different colormaps, 3D rendering). | MRtrix3 mrview, FSLeyes, DSI Studio. |
| QC Rating Database/Spreadsheet | Tracks ratings and notes across all subjects and pathways. | CSV file with columns: SubjectID, Pathway1Rating, Pathway1Notes, etc. |
| Statistical Software | For analyzing the impact of QC on diffusion metrics and group analyses. | R (with tidyverse, psych), Python (with pandas, scipy, seaborn). |
| Standardized Neuroanatomy Atlas | Reference for verifying tract trajectories during inspection. | JHU White-Matter Tractography Atlas, MNI template. |
Validating TRACULA: Accuracy, Reproducibility, and Comparison to Other Tools
TRACULA (TRActs Constrained by UnderLying Anatomy) is a FreeSurfer tool for automated probabilistic reconstruction of major white matter pathways. Its accuracy is not absolute but is consistently high for large, well-defined tracts when validated against expert manual tractography and histological atlases. Accuracy diminishes for smaller, complex, or crossing fiber regions.
Table 1: Summary of Key Validation Study Findings for TRACULA
| Validation Method | Tract(s) Studied | Core Accuracy Metric | Reported Value / Finding | Key Study (Year) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Expert Manual Tractography | Corticospinal Tract (CST), Fornix, Uncinate Fasciculus (UF) | Spatial Overlap (Dice Coefficient) | CST: ~0.7, Fornix: ~0.5-0.6, UF: ~0.6 | Yendiki et al., 2011 (Initial Validation) |
| Histological Atlas Comparison | 18 Major Pathways | Volumetric Correlation | R² values ranging from 0.3 to 0.9 across tracts | Wassermann et al., 2016 |
| Test-Retest Reliability | Major Pathways | Intraclass Correlation (ICC) for FA, MD | ICC(FA) > 0.8 for most of CST, CC; lower for limbic tracts | Lankappa et al., 2017 |
| Cross-Platform Comparison | Arcuate Fasciculus (AF), IFOF, ILF | Spatial Overlap & FA correlation | Moderate overlap; high correlation of derived FA values |
Table 2: Factors Influencing TRACULA Accuracy
| Factor | Impact on Accuracy | Mitigation Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| Input Data Quality | High-resolution, high SNR dMRI data critically improves reconstruction. | Use ≥ 60 directions, b=1000-3000 s/mm², 1.5-2.5 mm isotropic voxels. |
| Anatomical Variability | Accuracy lower in populations with severe anatomical deviation (e.g., large tumors). | Visual inspection of pathstats outputs and underlying aparc+aseg segmentation is mandatory. |
| Tract Complexity | Lower accuracy for small, crossing, or hard-to-dissect tracts (e.g., Fornix, SLF). | Use complementary methods (e.g., manual ROI placement) for focal hypothesis testing. |
| FreeSurfer Recon Quality | Errors in recon-all directly propagate to TRACULA. |
Rigorous quality control of FreeSurfer cortical/subcortical outputs required. |
Detailed Experimental Protocols
Protocol 1: Validating TRACULA Against Expert Manual Dissection
Purpose: To establish the spatial concordance of TRACULA's automated reconstructions with the gold-standard of expert manual tractography.
Materials & Workflow:
- Dataset: Multi-direction dMRI and T1-weighted anatomical data from a cohort (e.g., HCP, local dataset).
- Expert Manual Tractography:
- Software: Use platforms like 3D Slicer (with SlicerDMRI) or MRtrix3.
- Method: Two independent raters place anatomically informed Regions of Interest (ROIs) based on established protocols (e.g., Wakana et al., 2007).
- Streamline Generation: Generate streamlines using deterministic (FACT) or probabilistic algorithms. Define a consensus expert bundle via intersection or averaging.
- TRACULA Processing:
- Run full FreeSurfer
recon-allon T1 data. - Process dMRI data through the TRACULA pipeline (
trac-all -prep,-path).
- Run full FreeSurfer
- Comparison & Metric Calculation:
- Convert expert and TRACULA pathways to binary masks.
- Calculate the Dice Similarity Coefficient (DSC):
DSC = 2 * |A ∩ B| / (|A| + |B|), where A=TRACULA mask, B=Expert mask. - Calculate mean distance (Hausdorff distance) between bundle surfaces.
TRACULA vs. Expert Manual Validation Workflow
Protocol 2: Atlas-Based Validation Using Histological Ground Truth
Purpose: To compare volumetric and topological properties of TRACULA pathways with authoritative histological atlases.
Materials & Workflow:
- Reference Atlas: Obtain a digital histological atlas (e.g., INDI/Purdue/WU-Minn HCP 360 atlas).
- Spatial Normalization: Non-linearly register the atlas to a standard space (e.g., MNI152).
- TRACULA in Template Space: Run TRACULA on a group of subjects in native space, then transform the resulting pathway probability maps to the same standard space.
- Comparison: Calculate the spatial correlation or overlap between the TRACULA group-averaged probability map and the atlas-defined binary mask for each tract. Perform linear regression of tract volumes (from TRACULA) against atlas-defined volumes.
The Scientist's Toolkit: TRACULA Validation Essentials
Table 3: Key Research Reagent Solutions & Materials
| Item / Solution | Function in Validation Studies |
|---|---|
| High-Quality Multi-Shell dMRI Data | Provides the angular and diffusion contrast resolution needed for accurate FOD estimation, which is critical for TRACULA's ball-and-sticks model. |
| FreeSurfer Software Suite (v7.3+) | Provides the fully integrated recon-all and trac-all pipelines. Essential for consistent anatomical segmentation and tract reconstruction. |
| Histological White Matter Atlas | Serves as a biological ground truth for comparing tract location, shape, and topology (e.g., HCP 360, Jülich Atlas). |
| Manual Tractography Platform | Software like MRtrix3, DSI Studio, or 3D Slicer is required to generate expert manual dissections for comparison. |
| Spatial Analysis Toolbox | Tools like FSL, ANTs, or SPM for performing non-linear registration between subject space, template space, and atlas space. |
| Python/Matlab with NiBabel/SPM | For custom scripting of quantitative comparisons (Dice, Hausdorff distance, correlation analyses) and batch processing. |
| Visualization Software | FreeView (FreeSurfer), TrackVis, or MRtrix3 for 3D visualization and qualitative inspection of reconstructed tracts. |
Within a broader thesis on automated white matter reconstruction, TRACULA represents a robust, anatomically-constrained method with validated accuracy for large association, projection, and commissural tracts. Its primary strength is reproducibility and avoidance of user bias in ROI placement. However, validation studies clearly define its limits: it is not a substitute for hypothesis-driven manual dissection in areas of complex fiber architecture. Therefore, the choice between automated (TRACULA) and manual methods must be guided by the specific research question and the tracts of interest.
Assessing Test-Retest Reliability for Longitudinal and Clinical Trials
Within the broader thesis on TRACULA (TRActs Constrained by UnderLying Anatomy) FreeSurfer automated white matter pathway reconstruction, establishing robust test-retest reliability is a foundational prerequisite for its application in longitudinal neuroscience studies and clinical trials. This document provides application notes and detailed protocols for assessing the reliability of TRACULA-derived diffusion MRI metrics, ensuring they are fit for purpose in detecting subtle, clinically meaningful changes over time.
Application Notes on Reliability in the TRACULA Context
TRACULA reconstructs major white matter pathways (e.g., Corticospinal tract, Uncinate fasciculus, Arcuate fasciculus) using global probabilistic tractography informed by anatomical priors from FreeSurfer's cortical segmentation. In longitudinal settings, reliability is confounded by instrumental, biological, and analytical variability. High test-retest reliability indicates that observed longitudinal changes are more likely to reflect true biological or treatment effects rather than measurement noise. Key metrics of interest include fractional anisotropy (FA), mean diffusivity (MD), and radial/axial diffusivities (RD/AD) averaged along each reconstructed pathway.
Table 1: Representative Test-Retest Reliability Coefficients for TRACULA-Derived FA Metrics (Hypothetical Data Pooled from Recent Literature).
| White Matter Pathway | ICC(3,1) (95% CI) | Coefficient of Variation (%) | Mean FA (Baseline) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Corticospinal Tract (CST) | 0.92 (0.88-0.95) | 1.8 | 0.48 |
| Uncinate Fasciculus (UF) | 0.88 (0.82-0.92) | 2.5 | 0.41 |
| Arcuate Fasciculus (AF) | 0.85 (0.79-0.90) | 2.9 | 0.43 |
| Inferior Longitudinal Fasciculus (ILF) | 0.89 (0.84-0.93) | 2.2 | 0.44 |
| Forceps Major | 0.94 (0.91-0.96) | 1.5 | 0.50 |
ICC: Intraclass Correlation Coefficient; Model 3 (consistency), single measurement.
Table 2: Impact of FreeSurfer Cross-Sectional vs. Longitudinal Processing Streams on Reliability.
| Processing Pipeline | Mean ICC across 10 Pathways | Average MD CV% | Recommended Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|
| FreeSurfer Cross-Sectional (recon-all) | 0.86 | 2.8 | Baseline studies |
| FreeSurfer Longitudinal (base-template) | 0.91 | 2.1 | Longitudinal/Clinical Trials |
Experimental Protocols
Protocol 3.1: Test-Retest Reliability Study for TRACULA Metrics
Objective: To quantify the within-subject, between-session reliability of diffusion metrics from TRACULA-reconstructed pathways. Design: Prospective, same-subject repeat scanning. Participants: N ≥ 20 healthy volunteers. Include a broad age range relevant to the target clinical population. Scanning Schedule: Two identical MRI sessions spaced 1-4 weeks apart to minimize biological plasticity. MRI Acquisition:
- Scanner: 3T MRI with consistent hardware/software.
- Sequence: Single-shell or multi-shell diffusion-weighted imaging.
- Parameters: b=1000 or 2000 s/mm²; 64+ diffusion directions; 2.0mm³ isotropic voxels; TE/TR minimized.
- Ancillary: High-resolution T1-weighted MPRAGE (1mm³) for FreeSurfer anatomy. Processing:
- Preprocessing: Denoise, correct for eddy currents, motion, and susceptibility distortions using tools like FSL's eddy and topup.
- Anatomical Processing: Run the FreeSurfer longitudinal stream (
recon-all -base) to create an unbiased within-subject template, followed byrecon-all -longfor each time point. - TRACULA Reconstruction: Execute the TRACULA pipeline (
trac-all -prep,-path) using the longitudinal FreeSurfer outputs as the anatomical priors. - Metric Extraction: Use
trac-all -statto export mean FA, MD, RD, AD for each pathway (e.g.,lh.cst_AS). Statistical Analysis:
- Calculate Intraclass Correlation Coefficient (ICC(3,1)) for each pathway metric using a two-way mixed-effects model for consistency.
- Compute the Coefficient of Variation (CV%) as (within-subject standard deviation / grand mean) * 100.
- Determine the Smallest Detectable Change (SDC = 1.96 * √2 * within-subject standard deviation).
Protocol 3.2: Integrating TRACULA Reliability Assessment into a Clinical Trial Workflow
Objective: To establish a quality-controlled pipeline for deriving longitudinal white matter integrity endpoints in a multi-center neurotherapeutic trial. Phases:
- Pre-Trial Harmonization: Conduct a phantom and traveling human subject study across all trial sites to harmonize DWI acquisition protocols.
- Baseline Processing: Upon data receipt, run the full Protocol 3.1 (longitudinal stream) for each subject's baseline scan. Perform visual quality control (QC) of tract reconstructions.
- Interim & Exit Processing: As follow-up scans arrive, process them through the longitudinal pipeline locked to the subject's base template.
- Reliability Monitoring: Calculate the intra-subject variance of placebo-group subjects who show no clinical progression (as a proxy for test-retest noise) at interim analysis to refine sample size projections.
Diagrams
Title: Test-Retest Reliability Assessment Workflow for TRACULA
Title: Clinical Trial Pipeline with Integrated TRACULA QC Steps
The Scientist's Toolkit: Research Reagent Solutions
Table 3: Essential Software & Data Resources for TRACULA Reliability Studies.
| Resource Name | Type/Category | Function in Reliability Assessment |
|---|---|---|
| FreeSurfer (v7.3.2+) | Software Suite | Provides cortical/subcortical segmentations and the longitudinal processing stream critical for reducing anatomical noise in repeated measures. |
| TRACULA Package | FreeSurfer Tool | Automated, anatomically-constrained tractography for consistent reconstruction of specific white matter pathways across sessions. |
| FSL (FMRIB Software Library) | Software Suite | Primary tool for diffusion MRI preprocessing (eddy current, motion correction, distortion correction) to minimize non-biological variance. |
| DINAA (Diffusion Imaging in Python) | Software Library | Alternative for advanced diffusion modeling and quality assessment of DWI data prior to TRACULA. |
| ADNI-3 DWI Protocol | Imaging Protocol | Reference, publicly vetted acquisition protocol for multi-site reliability; serves as a harmonization template. |
| XTRACT Atlas (FMRIB) | Atlas Resource | Alternative white matter atlas for comparative analysis or validation of TRACULA's pathway definitions. |
| Qoala-T Tool | Quality Control Tool | Machine learning-based QC for FreeSurfer outputs, ensuring reliability of the anatomical priors fed into TRACULA. |
ICC Calculator (R irr package) |
Statistical Tool | Computes Intraclass Correlation Coefficients and confidence intervals for quantifying reliability metrics. |
This document provides detailed protocols and analyses for a thesis investigating automated versus manual white matter tractography, focusing on FreeSurfer's TRACULA (TRActs Constrained by UnderLying Anatomy).
Quantitative Comparison of Methodologies
Table 1: Performance Metrics: TRACULA vs. Manual Tractography
| Metric | TRACULA (Automated) | Manual (Expert-Driven) | Notes / Implications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Inter-Subject Reproducibility | High (ICC > 0.85) | Moderate to Low (ICC: 0.5 - 0.7) | Automation minimizes operator-dependent variance. |
| Intra-Rater Reliability | Not Applicable (Fully Automated) | Variable (High expertise required) | Manual methods suffer from intra-rater drift. |
| Processing Time per Subject | ~24-48 hrs (Hands-off) | ~4-8 hrs (Hands-on, per tract) | TRACULA offers scalability for large cohorts (N>100). |
| Sensitivity to Anatomical Variants | Low (Uses population priors) | High (Expert can adjust) | TRACULA may fail in severe pathologies or anomalies. |
| Required Expertise Level | Low (Proficiency in pipeline execution) | Very High (Neuroanatomy, MRI physics) | TRACULA democratizes access to tractography. |
| Output Consistency | Standardized across studies | Lab/Protocol dependent | TRACULA facilitates multi-site research comparisons. |
| Capacity for Novel Tract Discovery | None (Pre-defined tracts only) | High (Unconstrained exploration) | Manual is essential for hypothesis-generating research. |
Table 2: Common Biomarker Outputs and Their Clinical Research Relevance
| Biomarker | Typical Use in Drug Development | Methodological Consideration |
|---|---|---|
| Fractional Anisotropy (FA) | Quantifying white matter integrity; tracking treatment effects in neurodegenerative trials (e.g., MS, ALS). | TRACULA provides robust average FA per tract. Manual ROI placement can yield higher per-region sensitivity. |
| Mean Diffusivity (MD) | Assessing edema, inflammation, or neurodegeneration. | Both methods can extract MD. TRACULA reduces variance in longitudinal analysis. |
| Tract Volume | Monitoring atrophy or hypertrophy in response to therapy. | Sensitive to segmentation and stopping criteria. Manual methods offer more explicit control. |
| Radial/Axial Diffusivity | Hypothesizing on specific pathological processes (demyelination vs. axonal injury). | Reliable extraction requires high-quality data; TRACULA standardization reduces noise. |
Detailed Experimental Protocols
Protocol A: TRACULA Pipeline Execution for Multi-Subject Cohort Analysis Objective: To reconstruct 18 major white matter pathways consistently across a large subject cohort.
- Input Data Preparation:
- Acquire high-resolution T1-weighted (e.g., MPRAGE) and high-angular-resolution diffusion-weighted (minimum 64 directions, b=1000-3000 s/mm²) MRI scans.
- Ensure data conforms to BIDS (Brain Imaging Data Structure) format for seamless processing.
- FreeSurfer/TRACULA Setup:
- Install FreeSurfer (version 7.4.1 or later) and configure the
FREESURFER_HOMEenvironment variable. - Source the FreeSurfer setup script:
source $FREESURFER_HOME/SetUpFreeSurfer.sh. - Set the
SUBJECTS_DIRto your output directory.
- Install FreeSurfer (version 7.4.1 or later) and configure the
- Preprocessing & Reconstruction:
- Run the TRACULA pipeline using the
trac-allcommand with a predefined configuration (trac-all -prep -c <config_file>). - Key
configparameters:dwidir(DWI data path),fsdir(FreeSurfer recon directory),bet(brain extraction flag),ncpu(for parallel processing).
- Run the TRACULA pipeline using the
- Output & Quality Control:
- Find outputs in
$SUBJECTS_DIR/<subject_id>/dpath/. - Visually inspect
*pathstats.overall.txtfiles and thepngoverlays of each tract on the T1 image for obvious errors. - Use
trac-all -statto compile group statistics into tab-delimited files for analysis (e.g.,lh.ilf_FA.txt).
- Find outputs in
Protocol B: Expert Manual Tractography for Hypothesis Testing Objective: To delineate a specific white matter tract (e.g., Uncinate Fasciculus) with high precision for focal analysis.
- Data Preprocessing (Independent of TRACULA):
- Perform distortion correction and eddy-current correction on DWI data using FSL
topupandeddy. - Fit diffusion tensors or a ball-and-sticks model using FSL
dtifitorbedpostx.
- Perform distortion correction and eddy-current correction on DWI data using FSL
- Region of Interest (ROI) Definition:
- Co-register individual T1 to diffusion space using FSL
flirtorbbregister. - Manually draw ROI(s) on the FA map or co-registered T1 using software like ITK-SNAP or FSLeyes.
- For the Uncinate Fasciculus: Draw a "seed" ROI in the temporal stem and a "waypoint" ROI in the lateral frontal lobe, based on prior anatomical knowledge.
- Use an "AND" logic gate: only streamlines passing through both ROIs are retained.
- Co-register individual T1 to diffusion space using FSL
- Fiber Tracking & Refinement:
- Execute probabilistic tractography (e.g., FSL
probtrackx2) using the defined ROIs. - Apply biologically plausible constraints: set curvature threshold (~0.2), generate 5000-10000 samples per seed voxel.
- Threshold the resultant connectivity distribution to remove spurious connections (e.g., keep top 20% of streamlines).
- Execute probabilistic tractography (e.g., FSL
- Biomarker Extraction:
- Create a binary mask from the thresholded streamline bundle.
- Use
fslstatsto extract mean FA, MD, and volume from this mask.
Visualizations
Diagram 1: TRACULA Automated Pipeline Workflow
Diagram 2: Manual vs. Automated Method Selection Logic
The Scientist's Toolkit: Key Research Reagent Solutions
| Item / Solution | Function in Tractography Research |
|---|---|
| FreeSurfer Suite (with TRACULA) | Integrated software environment for automated cortical reconstruction and white matter tractography. Provides standardized pipelines. |
| FSL (FMRIB Software Library) | Essential for manual tractography, DWI preprocessing (eddy, topup), model fitting (dtifit, bedpostx), and tracking (probtrackx). |
| High-Angular Resolution DWI Data | The primary input data. 64+ diffusion directions and multiple b-values are crucial for accurate modeling of complex fiber geometries. |
| Anatomical Prior Probability Maps | Used by TRACULA to constrain tract reconstruction. These are spatial maps derived from a training set, defining likely pathway locations. |
| ITK-SNAP / FSLeyes | Interactive software for manual Region of Interest (ROI) delineation on structural and diffusion-weighted images. |
| BIDS Validator | Ensures neuroimaging data is organized according to the Brain Imaging Data Structure, promoting reproducibility and pipeline interoperability. |
| Cluster/Cloud Computing Access | Necessary for processing large cohorts with computationally intensive methods like TRACULA or bedpostx/probtrackx. |
Comparison to Other Automated Tools (e.g., FSL's Probtrackx, MRtrix3)
Application Notes
TRACULA (TRActs Constrained by UnderLying Anatomy) is a FreeSurfer-based automated pipeline for probabilistic reconstruction of major white matter pathways. It distinguishes itself through its strong anatomical prior approach. Unlike FSL's Probtrackx and MRtrix3's tractography tools, which are primarily voxel-based, TRACULA leverages FreeSurfer's high-quality cortical parcellation and subcortical segmentation to constrain tract trajectories from the outset. This anatomical guidance, derived from each subject's T1-weighted image, aims to reduce false positives and increase biological plausibility, particularly in crossing fiber regions. Key comparative metrics include sensitivity to crossing fibers, computational efficiency, dependency on accurate anatomical registration, and usability for longitudinal or clinical studies.
Table 1: Quantitative Comparison of Automated Tractography Tools
| Feature | TRACULA (FreeSurfer) | Probtrackx (FSL) | MRtrix3 (e.g., tckgen) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Core Methodology | Global, anatomy-constrained probabilistic | Voxel-wise probabilistic tracking | Anatomically Constrained Tractography (ACT) + spherical deconvolution |
| Primary Input | Diffusion data + FreeSurfer anatomical output | Diffusion data (often aligned to structural) | Diffusion data (+ T1 for ACT) |
| Anatomical Priors | Strong: Built-in from FreeSurfer parcellation. | Weak/User-defined: Requires manual ROI creation. | Moderate: ACT uses tissue types from segmented T1. |
| Handling Crossing Fibers | Relies on anatomical priors to navigate crossings. | Uses bedpostx multi-fiber model; crossings can still confound tracking. | Advanced: Uses Constrained Spherical Deconvolution (CSD) to model multiple fiber orientations. |
| Default Output | Probability distributions for ~18 predefined tracts. | Streamlines from user-defined seed/target ROIs. | Whole-brain streamline file; tract segmentation requires further steps. |
| Computational Load | High (due to integrated FreeSurfer processing) | Moderate to High (scales with number of seeds/voxels) | Moderate (CSD preprocessing is intensive) |
| Usability for Longitudinal Studies | High: Native integration with FreeSurfer longitudinal pipeline. | Moderate: Requires careful longitudinal registration of ROIs. | Moderate: Requires longitudinal processing of T1 for consistent ACT. |
| Key Strength | Reproducibility and minimal need for manual ROI delineation. | Flexibility in testing custom pathways and hypotheses. | High anatomical accuracy and specificity in complex white matter. |
| Primary Limitation | Limited to predefined set of tracts; less flexible. | Vulnerable to false positives; requires expert ROI placement. | Steeper learning curve; parameter tuning is critical. |
Experimental Protocols
Protocol 1: Standard TRACULA Reconstruction for Cohort Analysis Objective: To reconstruct major white matter pathways for a group of subjects for subsequent group comparison (e.g., patients vs. controls).
- Data Acquisition: Acquire high-resolution T1-weighted (e.g., MPRAGE) and high angular resolution diffusion-weighted (HARDI, min 60 directions, b=1000-3000 s/mm²) MRI data.
- FreeSurfer Reconstruction: Process each subject's T1 data through the standard FreeSurfer
recon-allpipeline to obtain cortical parcellations (aparc+aseg.mgz) and surface models. - Diffusion Data Preprocessing: Run
drbregisterto register diffusion images to FreeSurfer anatomical space. Usebedpostx(from FSL) to model diffusion parameters within the TRACULA framework. - TRACULA Configuration & Execution: Configure the
trac-all -prepstage to set paths and check data. Then runtrac-all -pathto perform the actual pathway reconstructions using the built-in anatomical priors. - Output Analysis: Extract tract-wise diffusion metrics (FA, MD, RD, AD) from each reconstructed pathway using TRACULA's
trac-all -statcommands for downstream statistical analysis.
Protocol 2: Comparative Validation Against Ground Truth (Phantom or Dissection) Objective: To quantify the accuracy of TRACULA versus Probtrackx and MRtrix3.
- Dataset: Use a publicly available digital phantom (e.g., FiberCup) or a dataset with known tract anatomy (e.g., post-mortem validation).
- Uniform Preprocessing: Align all tools to the same anatomical space. Use the same brain mask and, where applicable, the same seed/target definitions.
- Tool-Specific Execution:
- TRACULA: Run standard pipeline, extracting the tract most closely corresponding to the ground truth bundle.
- Probtrackx: Define seed, waypoint, and exclusion masks based on the known anatomy. Run with a high number of samples (e.g., 5000 per seed voxel).
- MRtrix3: Compute CSD response functions and fiber orientations. Generate whole-brain tractography with the
iFOD2algorithm and ACT. Use the same ROIs as Probtrackx to segment the target tract viatckedit.
- Validation Metrics: Calculate overlap (Dice coefficient), false-positive rate, and bundle coverage against the known ground truth bundle for each tool's output.
Protocol 3: Clinical Application in a Drug Trial for Neurodegeneration Objective: To assess white matter integrity changes as a potential biomarker in a clinical trial.
- Longitudinal Design: Acquire T1 and HARDI data at baseline, 6-month, and 12-month visits for both placebo and active treatment arms.
- Processing: Process all timepoints through the FreeSurfer longitudinal stream (
recon-all -long), then through TRACULA using the longitudinal anatomical base. - Tract of Interest Focus: Pre-select tracts implicated in the disease (e.g., fornix in Alzheimer's, corticospinal tract in ALS). Extract mean diffusivity (MD) and fractional anisotropy (FA) along each tract.
- Analysis: Use linear mixed-effects models to compare the rate of change in diffusion metrics between treatment groups, using TRACULA's inter-subject alignment of tract profiles as the dependent variable.
Visualizations
Title: TRACULA Processing Pipeline Overview
Title: Core Methodological Differences Between Tools
The Scientist's Toolkit
Table 2: Essential Research Reagent Solutions for Comparative Tractography Studies
| Item | Function in Research |
|---|---|
| FreeSurfer Software Suite | Provides the anatomical cortex and subcortex segmentation that forms the essential prior for TRACULA. Mandatory for this method. |
| FSL (FMRIB Software Library) | Contains bedpostx for multi-fiber modeling (used by TRACULA) and Probtrackx for direct comparative voxel-based probabilistic tracking. |
| MRtrix3 | Software for advanced diffusion analysis, notably Constrained Spherical Deconvolution (CSD) and anatomically constrained tractography, representing the state-of-the-art in fiber modeling. |
| High-Quality T1 & HARDI Data | The primary input. HARDI (≥60 directions) is critical for resolving crossing fibers, especially for MRtrix3 CSD and bedpostx. |
| Digital Phantom Datasets (e.g., FiberCup) | Provide ground truth for validating and comparing the accuracy and false-positive rates of different tractography algorithms. |
| Standardized Template ROIs (e.g., JHU Atlas) | Used as seed/target regions for Probtrackx and MRtrix3 to ensure comparability of reconstructed tracts across tools and studies. |
| Post-Processing Scripts (Python/Matlab) | Essential for extracting, comparing, and visualizing diffusion metrics (FA, MD) from the different output formats of each tool. |
| Computational Cluster Access | Tractography, especially probabilistic methods and CSD, is computationally intensive and requires significant processing power and storage. |
Introduction Within a broader thesis on automated white matter pathway reconstruction, TRACULA (TRActs Constrained by UnderLying Anatomy) in FreeSurfer represents a seminal method for probabilistic diffusion MRI tractography. Its application is pivotal for standardizing analyses in neuroscience research and therapeutic development. These Application Notes delineate its optimal use cases and constraints.
Core Principles and Comparative Data TRACULA leverages prior anatomical information from FreeSurfer's T1-weighted segmentation to constrain probabilistic tractography, reducing false positives. The table below summarizes its quantitative performance against generic alternatives.
Table 1: Performance Comparison of TRACULA vs. Unconstrained Tractography
| Metric | TRACULA | Unconstrained Probabilistic Tractography |
|---|---|---|
| Test-Retest Reliability (ICC) | High (0.75-0.95 for major pathways) | Moderate to Low (0.50-0.80) |
| Sensitivity to Crossing Fibers | Moderate (Uses bedpostx) | Moderate to High (Depends on model) |
| Dependency on T1 Quality | Critical | Low |
| Full Brain Tractography Time | ~24-48 hours (CPU-intensive) | ~5-15 hours |
| Required Manual Intervention | Low (Post-processing review) | Moderate (ROI definition, filtering) |
| Standardization | High (Automated, population-based priors) | Variable (Lab-specific protocols) |
Detailed Experimental Protocol: TRACULA Pipeline Protocol Title: Automated Reconstruction of 18 Major White Matter Pathways with TRACULA
Input Data Preparation:
- Acquire high-resolution T1-weighted MRI (e.g., MPRAGE, 1mm isotropic).
- Acquire diffusion-weighted MRI (e.g., single-shell or multi-shell, b-value=1000-3000 s/mm², ≥60 directions). Ensure gradient tables are correctly formatted.
- Preprocessing: Perform standard FSL
topupandeddycorrection for susceptibility distortion and eddy currents on DWI data.
FreeSurfer Anatomical Reconstruction:
- Run
recon-all -all -i <T1_file> -s <subject_id>on the T1-weighted volume. This 8-20 hour process generates cortical parcellations and subcortical segmentations essential for TRACULA's priors.
- Run
TRACULA Execution:
- Set environment:
export SUBJECTS_DIR=/path/to/freesurfer/subjects - Configure the
trac-allcommand: - Key configuration parameters (
<config_file>.conf):datadiff: Path to preprocessed DWI data.bvecfile&bvalfile: Diffusion gradient tables.dof: B-T1 registration degrees of freedom (recommend 6).npts: Number of path points (default 750).
- Set environment:
Output Analysis:
- Pathways are saved as path samples in
$SUBJECTS_DIR/<subject_id>/dpath/. - Extract diffusion-derived metrics (FA, MD, RD, AD) along each pathway using
trac-all -stator custom scripts.
- Pathways are saved as path samples in
Visualization: TRACULA Workflow Logic
Diagram Title: TRACULA Processing Pipeline Overview
The Scientist's Toolkit: Essential Research Reagents & Materials Table 2: Key Solutions for TRACULA-based Research
| Item | Function & Application Note |
|---|---|
| FreeSurfer Software Suite | Core platform for anatomical processing (recon-all) and housing the TRACULA module. |
| FSL (FMRIB Software Library) | Provides bedpostx for multi-fiber diffusion modeling and eddy/topup for DWI preprocessing. |
| High-Quality T1 & DWI Data | High-resolution (≤1mm³), high-SNR T1 and high angular resolution DWI (≥60 dir) are critical inputs. |
| Computational Cluster | Essential for processing; TRACULA is computationally intensive (CPU, RAM, storage). |
| Subject-Specific Template | For populations with atypical anatomy, a study-specific template may improve registration. |
| Alternative Software (e.g., MRtrix3, DSI Studio) | Necessary for comparison studies or when TRACULA's anatomical constraints are too restrictive. |
Decision Framework: When to Use TRACULA vs. Alternatives
Diagram Title: Decision Tree for TRACULA Use
Conclusion TRACULA is the tool of choice for automated, highly reproducible reconstruction of predefined major white matter tracts in neurotypical populations or studies where standardization outweighs exploratory analysis. Its limitations—heavy reliance on T1 anatomy, computational cost, and inability to discover novel pathways—necessitate consideration of alternative tractography software (e.g., MRtrix3, DSI Studio) for studies focused on clinical populations with severe anatomical disruption, novel pathway discovery, or whole-brain connectomics.
Conclusion
TRACULA represents a significant advancement in making robust, anatomy-constrained white matter tractography accessible for large-scale, reproducible research. By automating a complex process with strong anatomical priors, it reduces inter-rater variability and accelerates analysis—key benefits for multisite clinical studies and pharmaceutical trials investigating neurological disorders. While it may offer less flexibility than fully manual methods, its standardization is its greatest strength for hypothesis testing across populations. Future developments integrating machine learning for improved priors and compatibility with newer diffusion models promise to further solidify its role in the quantitative neuroimaging toolkit, ultimately enhancing our ability to map brain connectivity in health and disease.